Delivery systems for the direct application of siRNAs to induce RNA interference (RNAi) in vivo
- PMID: 17057369
- PMCID: PMC1559929
- DOI: 10.1155/JBB/2006/71659
Delivery systems for the direct application of siRNAs to induce RNA interference (RNAi) in vivo
Abstract
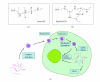
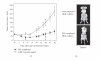
RNA interference (RNAi) is a powerful method for specific gene silencing which may also lead to promising novel therapeutic strategies. It is mediated through small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) which sequence-specifically trigger the cleavage and subsequent degradation of their target mRNA. One critical factor is the ability to deliver intact siRNAs into target cells/organs in vivo. This review highlights the mechanism of RNAi and the guidelines for the design of optimal siRNAs. It gives an overview of studies based on the systemic or local application of naked siRNAs or the use of various nonviral siRNA delivery systems. One promising avenue is the the complexation of siRNAs with the polyethylenimine (PEI), which efficiently stabilizes siRNAs and, upon systemic administration, leads to the delivery of the intact siRNAs into different organs. The antitumorigenic effects of PEI/siRNA-mediated in vivo gene-targeting of tumor-relevant proteins like in mouse tumor xenograft models are described.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Gene silencing through RNA interference (RNAi) in vivo: strategies based on the direct application of siRNAs.J Biotechnol. 2006 Jun 25;124(1):12-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2005.12.003. Epub 2006 Jan 18. J Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 16413079 Review.
-
RNA interference-mediated gene silencing of pleiotrophin through polyethylenimine-complexed small interfering RNAs in vivo exerts antitumoral effects in glioblastoma xenografts.Hum Gene Ther. 2006 Jul;17(7):751-66. doi: 10.1089/hum.2006.17.751. Hum Gene Ther. 2006. PMID: 16839274
-
RNAi-mediated gene-targeting through systemic application of polyethylenimine (PEI)-complexed siRNA in vivo.Gene Ther. 2005 Mar;12(5):461-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3302425. Gene Ther. 2005. PMID: 15616603
-
Polyethylenimines for RNAi-mediated gene targeting in vivo and siRNA delivery to the lung.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011 Apr;77(3):438-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2010.11.007. Epub 2010 Nov 18. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011. PMID: 21093588 Review.
-
A low molecular weight fraction of polyethylenimine (PEI) displays increased transfection efficiency of DNA and siRNA in fresh or lyophilized complexes.J Control Release. 2006 May 15;112(2):257-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2006.02.009. Epub 2006 Mar 6. J Control Release. 2006. PMID: 16574264
Cited by
-
MEMS-enabled implantable drug infusion pumps for laboratory animal research, preclinical, and clinical applications.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012 Nov;64(14):1628-38. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.08.006. Epub 2012 Aug 19. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012. PMID: 22926321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mannosylated bioreducible nanoparticle-mediated macrophage-specific TNF-α RNA interference for IBD therapy.Biomaterials. 2013 Oct;34(30):7471-82. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.06.008. Epub 2013 Jun 29. Biomaterials. 2013. PMID: 23820013 Free PMC article.
-
Notch1 is a p53 target gene involved in human keratinocyte tumor suppression through negative regulation of ROCK1/2 and MRCKalpha kinases.Genes Dev. 2007 Mar 1;21(5):562-77. doi: 10.1101/gad.1484707. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 17344417 Free PMC article.
-
Recognizing and avoiding siRNA off-target effects for target identification and therapeutic application.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010 Jan;9(1):57-67. doi: 10.1038/nrd3010. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010. PMID: 20043028 Review.
-
RNA interference targeting survivin exerts antitumoral effects in vitro and in established glioma xenografts in vivo.Neuro Oncol. 2011 Oct;13(10):1074-89. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nor098. Epub 2011 Jul 25. Neuro Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21788344 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cech TR, Zaug AJ, Grabowski PJ. In vitro splicing of the ribosomal RNA precursor of Tetrahymena: involvement of a guanosine nucleotide in the excision of the intervening sequence. Cell. 1981;27(3 pt 2):487–496. - PubMed
-
- Kruger K, Grabowski PJ, Zaug AJ, Sands J, Gottschling DE, Cech TR. Self-splicing RNA: autoexcision and autocyclization of the ribosomal RNA intervening sequence of Tetrahymena. Cell. 1982;31(1):147–157. - PubMed
-
- Guerrier-Takada C, Gardiner K, Marsh T, Pace N, Altman S. The RNA moiety of ribonuclease P is the catalytic subunit of the enzyme. Cell. 1983;35(3 pt 2):849–857. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

