SNP-PHAGE--High throughput SNP discovery pipeline
- PMID: 17059604
- PMCID: PMC1626092
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-468
SNP-PHAGE--High throughput SNP discovery pipeline
Abstract
Background: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) as defined here are single base sequence changes or short insertion/deletions between or within individuals of a given species. As a result of their abundance and the availability of high throughput analysis technologies SNP markers have begun to replace other traditional markers such as restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs), amplified fragment length polymorphisms (AFLPs) and simple sequence repeats (SSRs or microsatellite) markers for fine mapping and association studies in several species. For SNP discovery from chromatogram data, several bioinformatics programs have to be combined to generate an analysis pipeline. Results have to be stored in a relational database to facilitate interrogation through queries or to generate data for further analyses such as determination of linkage disequilibrium and identification of common haplotypes. Although these tasks are routinely performed by several groups, an integrated open source SNP discovery pipeline that can be easily adapted by new groups interested in SNP marker development is currently unavailable.
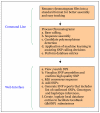
Results: We developed SNP-PHAGE (SNP discovery Pipeline with additional features for identification of common haplotypes within a sequence tagged site (Haplotype Analysis) and GenBank (-dbSNP) submissions. This tool was applied for analyzing sequence traces from diverse soybean genotypes to discover over 10,000 SNPs. This package was developed on UNIX/Linux platform, written in Perl and uses a MySQL database. Scripts to generate a user-friendly web interface are also provided with common queries for preliminary data analysis. A machine learning tool developed by this group for increasing the efficiency of SNP discovery is integrated as a part of this package as an optional feature. The SNP-PHAGE package is being made available open source at http://bfgl.anri.barc.usda.gov/ML/snp-phage/.
Conclusion: SNP-PHAGE provides a bioinformatics solution for high throughput SNP discovery, identification of common haplotypes within an amplicon, and GenBank (dbSNP) submissions. SNP selection and visualization are aided through a user-friendly web interface. This tool is useful for analyzing sequence tagged sites (STSs) of genomic sequences, and this software can serve as a starting point for groups interested in developing SNP markers.
Figures

References
-
- http: www.phrap.org Phrap. 2006. http://www.phrap.org
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

