MyoD-positive epiblast cells regulate skeletal muscle differentiation in the embryo
- PMID: 17060497
- PMCID: PMC2064569
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200605037
MyoD-positive epiblast cells regulate skeletal muscle differentiation in the embryo
Abstract
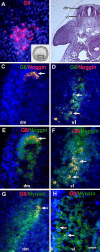
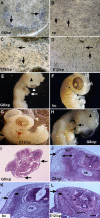
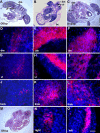
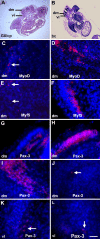
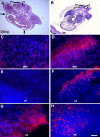
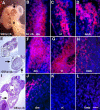
MyoD mRNA is expressed in a subpopulation of cells within the embryonic epiblast. Most of these cells are incorporated into somites and synthesize Noggin. Ablation of MyoD-positive cells in the epiblast subsequently results in the herniation of organs through the ventral body wall, a decrease in the expression of Noggin, MyoD, Myf5, and myosin in the somites and limbs, and an increase in Pax-3-positive myogenic precursors. The addition of Noggin lateral to the somites compensates for the loss of MyoD-positive epiblast cells. Skeletal muscle stem cells that arise in the epiblast are utilized in the somites to promote muscle differentiation by serving as a source of Noggin.
Figures

References
-
- Amthor, H., B. Christ, and K. Patel. 1999. A molecular mechanism enabling continuous embryonic muscle growth-a balance between proliferation and differentiation. Development. 126:1041–1053. - PubMed
-
- Baker, C.V.H., M.R. Stark, C. Marcelle, and M. Bronner-Fraser. 1999. Competence, specification and induction of Pax-3 in the trigeminal placode. Development. 126:147–156. - PubMed
-
- Bate, M. 1990. The embryonic development of larval muscles in Drosophila. Development. 110:791–804. - PubMed
-
- Baylies, M.K., and A.M. Michelson. 2001. Invertebrate myogenesis: looking back to the future of muscle development. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 11:431–439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

