Activity of ribavirin against Hantaan virus correlates with production of ribavirin-5'-triphosphate, not with inhibition of IMP dehydrogenase
- PMID: 17060520
- PMCID: PMC1797647
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00790-06
Activity of ribavirin against Hantaan virus correlates with production of ribavirin-5'-triphosphate, not with inhibition of IMP dehydrogenase
Abstract
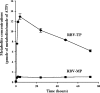
Ribavirin (RBV) is a broad-spectrum antiviral agent that inhibits the production of infectious Hantaan virus (HTNV). Although the mechanism of action of RBV against HTNV is not understood, RBV is metabolized in human cells to both RBV-5'-monophosphate, which inhibits IMP dehydrogenase, resulting in a decrease in intracellular GTP levels, and RBV-5'-triphosphate (RBV-TP), which could selectively interact with the viral RNA polymerase. To elucidate which activity of RBV was most important to its anti-HTNV activity, the mechanism of action of RBV was studied in Vero E6 cells. Incubation with 10 to 40 mug/ml RBV resulted in a small decrease in GTP levels that was not dose dependent. Increasing the RBV concentration from 10 to 40 mug/ml resulted in a decrease in viral RNA (vRNA) levels and an increase in RBV-TP formation. Mycophenolic acid (MPA), an inhibitor of IMP dehydrogenase, also resulted in a decrease in vRNA levels; however, treatment with MPA resulted in a much greater decrease in GTP levels than that seen with RBV. Treatment with both MPA and RBV resulted in increased reduction of vRNA levels but did not result in enhanced depression of GTP levels. Although guanosine prevented the depression in GTP levels caused by RBV, guanosine only partially prevented the effect of RBV on vRNA levels. These results suggest that the inhibition of IMP dehydrogenase by RBV is of secondary importance to the inhibition of vRNA replication by RBV and that the interaction of RBV-TP with the viral polymerase is the primary action of RBV.
Figures
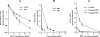
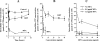

References
-
- Balzarini, J., A. Karlsson, L. Wang, C. Bohman, K. Horska, I. Votruba, A. Fridland, A. Van Aerschot, P. Herdewijn, and E. De Clercq. 1993. Eicar (5-ethynyl-1-beta-d-ribofuranosylimidazole-4-carboxamide). A novel potent inhibitor of inosinate dehydrogenase activity and guanylate biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 268:24591-24598. - PubMed
-
- De Clercq, E. 1993. Antiviral agents: characteristic activity spectrum depending on the molecular target with which they interact. Adv. Virus Res. 42:1-55. - PubMed
-
- Gallois-Montbrun, S., Y. Chen, H. Dutartre, M. Sophys, S. Morera, C. Guerreiro, B. Schneider, L. Mulard, J. Janin, M. Veron, D. Deville-Bonne, and B. Canard. 2003. Structural analysis of the activation of ribavirin analogs by NDP kinase: comparison with other ribavirin targets. Mol. Pharmacol. 63:538-546. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

