Tactile guidance of prey capture in Etruscan shrews
- PMID: 17060642
- PMCID: PMC1621049
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0605573103
Tactile guidance of prey capture in Etruscan shrews
Abstract
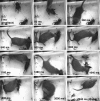
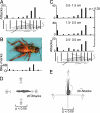
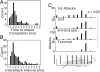
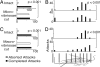
Whereas visuomotor behaviors and visual object recognition have been studied in detail, we know relatively little about tactile object representations. We investigate a new model system for the tactile guidance of behavior, namely prey (cricket) capture by one of the smallest mammals, the Etruscan shrew, Suncus etruscus. Because of their high metabolic rate and nocturnal lifestyle, Etruscan shrews are forced to detect, overwhelm, and kill prey in large numbers in darkness. Crickets are exquisitely mechanosensitive, fast-moving prey, almost as big as the shrew itself. Shrews succeed in hunting by lateralized, precise, and fast attacks. Removal experiments demonstrate that both macrovibrissae and microvibrissae are required for prey capture, with the macrovibrissae being involved in attack targeting. Experiments with artificial prey replica show that tactile shape cues are both necessary and sufficient for evoking attacks. Prey representations are motion- and size-invariant. Shrews distinguish and memorize prey features. Corrective maneuvers and cricket shape manipulation experiments indicate that shrew behavior is guided by Gestalt-like prey descriptions. Thus, tactile object recognition in Etruscan shrews shares characteristics of human visual object recognition, but it proceeds faster and occurs in a 20,000-times-smaller brain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Tinbergen N. The Study of Instinct. Oxford: Clarendon; 1951.
-
- von Uexküll JJ. Umwelt und Innenwelt der Tiere. Berlin: Springer; 1909.
-
- Ewert JP, Arend B, Becker V, Borchers HW. Brain Behav Evol. 1979;16:38–51. - PubMed
-
- Ewert JP. In: Comparative Neurology of the Optic Tectum. Vanegas H, editor. New York: Plenum; 1984. pp. 247–416.
-
- Treisman A, Gelade G. Cognit Psychol. 1980;12:97–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

