Ghrelin modulates the activity and synaptic input organization of midbrain dopamine neurons while promoting appetite
- PMID: 17060947
- PMCID: PMC1618869
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI29867
Ghrelin modulates the activity and synaptic input organization of midbrain dopamine neurons while promoting appetite
Abstract
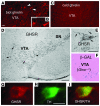
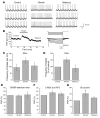
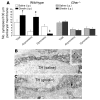
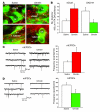
The gut hormone ghrelin targets the brain to promote food intake and adiposity. The ghrelin receptor growth hormone secretagogue 1 receptor (GHSR) is present in hypothalamic centers controlling energy metabolism as well as in the ventral tegmental area (VTA), a region important for motivational aspects of multiple behaviors, including feeding. Here we show that in mice and rats, ghrelin bound to neurons of the VTA, where it triggered increased dopamine neuronal activity, synapse formation, and dopamine turnover in the nucleus accumbens in a GHSR-dependent manner. Direct VTA administration of ghrelin also triggered feeding, while intra-VTA delivery of a selective GHSR antagonist blocked the orexigenic effect of circulating ghrelin and blunted rebound feeding following fasting. In addition, ghrelin- and GHSR-deficient mice showed attenuated feeding responses to restricted feeding schedules. Taken together, these data suggest that the mesolimbic reward circuitry is targeted by peripheral ghrelin to influence physiological mechanisms related to feeding.
Figures

References
-
- Van der Lely A.J., Tschop M., Heiman M.L., Ghigo E. Biological, physiological, pathophysiological, and pharmacological aspects of ghrelin. Endocr. Rev. 2004;25:426–457. - PubMed
-
- Kojima M., et al. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature. 1999;402:656–660. - PubMed
-
- Tschop M., Smiley D.L., Heiman M.L. Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature. 2000;407:908–913. - PubMed
-
- Nakazato M., et al. A role for ghrelin in the central regulation of feeding. Nature. 2001;409:194–198. - PubMed
-
- Cowley M.A., et al. The distribution and mechanism of action of ghrelin in the CNS demonstrates a novel hypothalamic circuit regulating energy homeostasis. Neuron. 2003;37:649–661. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS041725/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA015632/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK070723/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH014092/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK060711/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK074386/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MH014092/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH014092/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK069987/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK074386/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK056863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MH057483/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH057483/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG022880/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS041725/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DK056863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK069987/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AG022880/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK060711/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK070723/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

