Structural basis of the Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus MCM helicase activity
- PMID: 17062628
- PMCID: PMC1635305
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl708
Structural basis of the Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus MCM helicase activity
Abstract
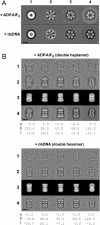
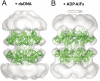
The MCM complex from the archaeon Methanother-mobacter thermautotrophicus is a model for the eukaryotic MCM2-7 helicase. We present electron-microscopy single-particle reconstructions of a DNA treated M.thermautotrophicus MCM sample and a ADP.AlF(x) treated sample, respectively assembling as double hexamers and double heptamers. The electron-density maps display an unexpected asymmetry between the two rings, suggesting that large conformational changes can occur within the complex. The structure of the MCM N-terminal domain, as well as the AAA+ and the C-terminal HTH dom-ains of ZraR can be fitted into the reconstructions. Distinct configurations can be modelled for the AAA+ and the HTH domains, suggesting the nature of the conformational change within the complex. The pre-sensor 1 and the helix 2 insertions, important for the activity, can be located pointing towards the centre of the channel in the presence of DNA. We propose a mechanistic model for the helicase activity, based on a ligand-controlled rotation of the AAA+ subunits.
Figures





References
-
- Chong J.P. Learning to unwind. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005;12:734–736. - PubMed
-
- Shechter D.F., Ying C.Y., Gautier J. The intrinsic DNA helicase activity of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum delta H minichromosome maintenance protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:15049–15059. - PubMed
-
- Fletcher R.J., Bishop B.E., Leon R.P., Sclafani R.A., Ogata C.M., Chen X.S. The structure and function of MCM from archaeal M. thermoautotrophicum. Nature Struct. Biol. 2003;10:160–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

