Psychopathology in young people with intellectual disability
- PMID: 17062861
- PMCID: PMC2422867
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.296.16.1981
Psychopathology in young people with intellectual disability
Erratum in
- JAMA. 2006 Dec 13;296(22):2682
Abstract
Context: Comorbid severe mental health problems complicating intellectual disability are a common and costly public health problem. Although these problems are known to begin in early childhood, little is known of how they evolve over time or whether they continue into adulthood.
Objective: To study the course of psychopathology in a representative population of children and adolescents with intellectual disability.
Design, setting, and participants: The participants of the Australian Child to Adult Development Study, an epidemiological cohort of 578 children and adolescents recruited in 1991 from health, education, and family agencies that provided services to children with intellectual disability aged 5 to 19.5 years in 6 rural and urban census regions in Australia, were followed up for 14 years with 4 time waves of data collection. Data were obtained from 507 participants, with 84% of wave 1 (1991-1992) participants being followed up at wave 4 (2002-2003).
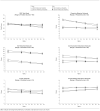
Main outcome measures: The Developmental Behaviour Checklist (DBC), a validated measure of psychopathology in young people with intellectual disability, completed by parents or other caregivers. Changes over time in the Total Behaviour Problem Score and 5 subscale scores of the DBC scores were modeled using growth curve analysis.
Results: High initial levels of behavioral and emotional disturbance decreased only slowly over time, remaining high into young adulthood, declining by 1.05 per year on the DBC Total Behaviour Problem Score. Overall severity of psychopathology was similar across mild to severe ranges of intellectual disability (with mean Total Behaviour Problem Scores of approximately 44). Psychopathology decreased more in boys than girls over time (boys starting with scores 2.61 points higher at baseline and ending with scores 2.57 points lower at wave 4), and more so in participants with mild intellectual disability compared with those with severe or profound intellectual disability who diverged from having scores 0.53 points lower at study commencement increasing to a difference of 6.98 points below severely affected children by wave 4. This trend was observed in each of the subscales, except the social-relating disturbance subscale, which increased over time. Prevalence of participants meeting criteria for major psychopathology or definite psychiatric disorder decreased from 41% at wave 1 to 31% at wave 4. Few of the participants (10%) with psychopathology received mental health interventions during the study period.
Conclusion: These results provide evidence that the problem of psychopathology comorbid with intellectual disability is both substantial and persistent and suggest the need for effective mental health interventions.
Figures
References
-
- Hodapp RM, Dykens EM. Mental retardation. In: Mash EJ, Barkley RA, editors. Child Psychopathology. Guilford; New York, NY: 1996. pp. 362–389.
-
- Dekker MC, Koot HM, van der Ende J, Verhulst FC. Emotional and behavioral problems in children and adolescents with and without intellectual disability. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2002;43:1087–1098. - PubMed
-
- Einfeld SL, Tonge BJ. Population prevalence of psychopathology in children and adolescents with intellectual disability, II: epidemiological findings. J Intellect Disabil Res. 1996;40:99–109. - PubMed
-
- Linna SL, Moilanen I, Ebeling H, et al. Psychiatric symptoms in children with intellectual disability. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1999;8(supp l4):77–82. - PubMed
-
- Richardson SA, Koller H. Twenty-Two Years: Causes and Consequences of Mental Retardation. Harvard University Press; Cambridge, Mass: 1996.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical