Triggers of inflammation after renal ischemia/reperfusion
- PMID: 17064966
- PMCID: PMC1888143
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2006.09.008
Triggers of inflammation after renal ischemia/reperfusion
Abstract
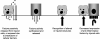
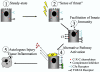
Renal ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) is a common cause of acute renal failure (ARF). Ischemic ARF is associated with tubulointerstitial inflammation, and studies using animal models have demonstrated that the inflammatory response to I/R exacerbates the resultant renal injury. Ischemic ARF involves complement activation, the generation of cytokines and chemokines within the kidney, and infiltration of the kidney by leukocytes. Recent work has revealed some of the events and signals that trigger the inflammatory response to aseptic, hypoxic injury of the kidney. In many ways, the inflammatory reaction to this injury resembles that seen during ascending urinary infection, and it may represent a general response of the tubular epithelial cells (TECs) to stress or injury. A greater understanding of the signals that trigger the inflammatory response may permit the development of effective therapies to ameliorate ischemic ARF.
Figures
References
-
- Thadhani R, Pascual M, Bonventre JV. Acute renal failure. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:1448–60. - PubMed
-
- Levy EM, Viscoli CM, Horwitz RI. The effect of acute renal failure on mortality. A cohort analysis, Jama. 1996;275:1489–94. - PubMed
-
- Liano F, Pascual J. Epidemiology of acute renal failure: a prospective, multicenter, community-based study. Madrid Acute Renal Failure Study Group, Kidney Int. 1996;50:811–8. - PubMed
-
- Chertow GM, Levy EM, Hammermeister KE, Grover F, Daley J. Independent association between acute renal failure and mortality following cardiac surgery. Am J Med. 1998;104:343–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

