Influenza Virus Database (IVDB): an integrated information resource and analysis platform for influenza virus research
- PMID: 17065465
- PMCID: PMC1781131
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl779
Influenza Virus Database (IVDB): an integrated information resource and analysis platform for influenza virus research
Abstract
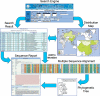
Frequent outbreaks of highly pathogenic avian influenza and the increasing data available for comparative analysis require a central database specialized in influenza viruses (IVs). We have established the Influenza Virus Database (IVDB) to integrate information and create an analysis platform for genetic, genomic, and phylogenetic studies of the virus. IVDB hosts complete genome sequences of influenza A virus generated by Beijing Institute of Genomics (BIG) and curates all other published IV sequences after expert annotation. Our Q-Filter system classifies and ranks all nucleotide sequences into seven categories according to sequence content and integrity. IVDB provides a series of tools and viewers for comparative analysis of the viral genomes, genes, genetic polymorphisms and phylogenetic relationships. A search system has been developed for users to retrieve a combination of different data types by setting search options. To facilitate analysis of global viral transmission and evolution, the IV Sequence Distribution Tool (IVDT) has been developed to display the worldwide geographic distribution of chosen viral genotypes and to couple genomic data with epidemiological data. The BLAST, multiple sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis tools were integrated for online data analysis. Furthermore, IVDB offers instant access to pre-computed alignments and polymorphisms of IV genes and proteins, and presents the results as SNP distribution plots and minor allele distributions. IVDB is publicly available at http://influenza.genomics.org.cn.
Figures
References
-
- Horimoto T., Kawaoka Y. Influenza: lessons from past pandemics, warnings from current incidents. Nature Rev. Microbiol. 2005;3:591–600. - PubMed
-
- Steinhauer D.A., Skehel J.J. Genetics of influenza viruses. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2002;36:305–332. - PubMed
-
- Obenauer J.C., Denson J., Mehta P.K., Su X., Mukatira S., Finkelstein D.B., Xu X., Wang J., Ma J., Fan Y., et al. Large-scale sequence analysis of avian influenza isolates. Science. 2006;311:1576–1580. - PubMed
-
- Ghedin E., Sengamalay N.A., Shumway M., Zaborsky J., Feldblyum T., Subbu V., Spiro D.J., Sitz J., Koo H., Bolotov P., et al. Large-scale sequencing of human influenza reveals the dynamic nature of viral genome evolution. Nature. 2005;437:1162–1166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

