Serum bactericidal activities of high-dose daptomycin with and without coadministration of gentamicin against isolates of Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus species
- PMID: 17065618
- PMCID: PMC1635189
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00290-06
Serum bactericidal activities of high-dose daptomycin with and without coadministration of gentamicin against isolates of Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus species
Abstract
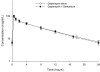
The purpose of this experiment was to evaluate the pharmacokinetics and serum bactericidal titers (SBTs) of daptomycin alone and in combination with gentamicin against strains of Staphylococcus aureus and enterococci to determine if there might be any benefit to the addition of the aminoglycoside. A multiple-dose, randomized crossover study was performed in 11 healthy volunteers to evaluate the steady-state pharmacokinetic profile of 6 mg/kg of body weight daptomycin once daily with or without 1 mg/kg gentamicin every 8 h. SBTs were determined against clinical isolates of nosocomial (MRSA 494) and community-acquired (CA-MRSA 44) methicillin-resistant S. aureus, vancomycin-susceptible Enterococcus faecalis (VSEF 49452), vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium (VREF 80), and quality control strains of methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (ATCC 29213) and vancomycin-susceptible E. faecalis (ATCC 29212). Enhancement of bactericidal activity was evaluated by calculating and comparing the areas under the bactericidal curve (AUBC) for each dosing regimen against each isolate. The area under the concentration-time curve from 0 to 24 h and clearance for daptomycin alone were 645 +/- 91 microg.h/ml and 9.47 +/- 1.4 mg/h/kg, respectively, compared with 642 +/- 69 microg.h/ml and 9.45 +/- 1.0 mg/h/kg for daptomycin plus gentamicin. Daptomycin alone displayed sustained bactericidal activity against five of the six isolates over the entire 24-h dosing interval; bactericidal activity was maintained for 8 h against VREF 80. Mean AUBCs for daptomycin alone ranged from 935 to 1,263 and 36 to 238 against staphylococcal and enterococcal isolates, respectively, compared with 902 to 972 and 34 to 213 against staphylococci and enterococci when coadministered with gentamicin. The results of this study suggest that the addition of gentamicin does not alter the pharmacokinetic profile or enhance the bactericidal activity of daptomycin against staphylococcal or enterococcal isolates.
Figures

References
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2005. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibilities tests for bacteria that grow aerobically—15th informational supplement. CLSI/NCCLS document M100-S15. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, Pa.
-
- Carpenter, C. F., and H. F. Chambers. 2004. Daptomycin: another novel agent for treating infections due to drug-resistant gram-positive pathogens. Clin. Infect. Dis. 38:994-1000. - PubMed
-
- Cockcroft, D. W., and M. H. Gault. 1976. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 16:31-41. - PubMed
-
- Dandekar, P. K., P. R. Tessier, P. Williams, C. H. Nightingale, and D. P. Nicolau. 2003. Pharmacodynamic profile of daptomycin against Enterococcus species and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a murine thigh infection model. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 52:405-411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

