Noninfectious papilloma virus-like particles inhibit HIV-1 replication: implications for immune control of HIV-1 infection by IL-27
- PMID: 17068156
- PMCID: PMC1801045
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-02-001578
Noninfectious papilloma virus-like particles inhibit HIV-1 replication: implications for immune control of HIV-1 infection by IL-27
Abstract
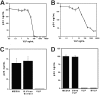
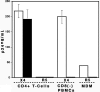
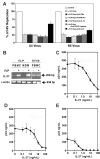
Human papilloma virus (HPV)-like particles (VLPs) have been used as a vaccine to prevent HPV infection. Recent studies demonstrate that VLPs bind to dendritic cells and induce the expression of antiviral cytokines such as interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha), interleukin-10 (IL-10) and IFN-gamma. In the present study, we evaluated the effect of VLPs on HIV-1 replication in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), CD4+ T cells, and macrophages. Here, we show that VLPs suppress the replication of both X4 and R5 HIV-1 without affecting the expression of CD4, CXCR4, and CCR5. Soluble factor(s) released by PBMCs and macrophages on VLPs treatment inhibited HIV-1 replication. To determine the inhibitory factors, DNA microarray analysis was performed using VLP-treated PBMCs and macrophages. VLPs induced the genes associated with IFN induction, immune responses, and antiviral responses, among with the recently described cytokine IL-27. Subsequently, IL-27 was found to be a potent inhibitor of HIV-1 replication in PBMCs, CD4+ T cells, and macrophages. Taken together, our studies identify a novel role of IL-27 in restricting HIV-1 replication and suggest that further examination of the inhibitory property of IL-27 may pave the way for a novel therapy for HIV-1 infection.
Figures


References
-
- Toso JF, Chen CH, Mohr JR, et al. Oligoclonal CD8 lymphocytes from persons with asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 infection inhibit HIV-1 replication. J Infect Dis. 1995;172:964–973. - PubMed
-
- Pinto LA, Sharpe S, Cohen DI, Shearer GM. Alloantigen-stimulated anti-HIV activity. Blood. 1998;92:3346–3354. - PubMed
-
- Wagner L, Yang OO, Garcia-Zepeda EA, et al. Beta-chemokines are released from HIV-1-specific cytolytic T-cell granules complexed to proteoglycans. Nature. 1998;391:908–911. - PubMed
-
- Price DA, Sewell AK, Dong T, et al. Antigen-specific release of beta-chemokines by anti-HIV-1 cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Curr Biol. 1998;8:355–358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

