Synchronized and noise-robust audio recordings during realtime magnetic resonance imaging scans
- PMID: 17069275
- PMCID: PMC1800830
- DOI: 10.1121/1.2335423
Synchronized and noise-robust audio recordings during realtime magnetic resonance imaging scans
Abstract
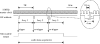
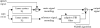
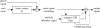
This letter describes a data acquisition setup for recording, and processing, running speech from a person in a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner. The main focus is on ensuring synchronicity between image and audio acquisition, and in obtaining good signal to noise ratio to facilitate further speech analysis and modeling. A field-programmable gate array based hardware design for synchronizing the scanner image acquisition to other external data such as audio is described. The audio setup itself features two fiber optical microphones and a noise-canceling filter. Two noise cancellation methods are described including a novel approach using a pulse sequence specific model of the gradient noise of the MRI scanner. The setup is useful for scientific speech production studies. Sample results of speech and singing data acquired and processed using the proposed method are given.
Figures



References
-
- Stone M, Davis E, Douglas A, NessAiver M, Gullapalli R, Levine W, Lundberg A. Modelling the motion of the internal tongue from tagged cine-MRI images. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2001;109:2974–2982. - PubMed
-
- Narayanan S, Nayak K, Sethy A, Byrd D. An approach to real-time magnetic resonance imaging for speech production. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2004;115:1771–1776. - PubMed
-
- NessAiver M, Stone M, Parthasarathy V, Kahana Y, Paritsky A. Recording high quality speech during tagged Cine MRI studies using a fiber optic microphone. J. Magn. Reson Imaging. 2006;23:92–97. - PubMed
-
- http://phone-or.com, last seen 02/28/2006.
-
- Kahana Y, Paritsky A, Kots A, Mican S. Recent advances in optical microphone technology. Proc. of the 32nd International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering 2003
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

