Association between the levels of biogenic amines and superoxide anion production in brain regions of rats after subchronic exposure to TCDD
- PMID: 17070641
- PMCID: PMC1987358
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2006.09.009
Association between the levels of biogenic amines and superoxide anion production in brain regions of rats after subchronic exposure to TCDD
Abstract
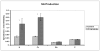
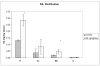
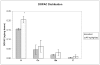
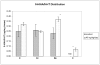
The effects of TCDD on the distribution of biogenic amines and production of superoxide anion (SA) in different brain regions of rats have been studied after subchronic exposure. Groups of females Sprague-Dawley rats were administered daily dose of 46ng TCDD/(kgday) (treated groups), or the vehicle used to dissolve TCDD (control group), for 90 days. The rats were sacrificed at the end of the exposure period and their brains were dissected into different regions including, hippocampus (H), cerebral cortex (Cc), cerebellum (C), and brain stem (Bs). The levels of different biogenic amines and some of their metabolites, including, norepinephrine (NE), dopamine (DA), 3,4-dihydroxy phenyl acetic acid (DOPAC), 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl acetic acid (HVA), 5-hydroxy tryptamine (5-HT), and 5-hydroxy indole 3-acetic acid (5-HIAA), were determined in those brain regions, using a high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) system with an electrochemical detector. SA production was also determined in those regions, using the cytochrome c reduction method. Results of analyses indicate significant increases in the levels of DA, NE and DOPAC in H, NE and HVA in Cc, NE and DA in Bs and NE in C. SA production was significantly increased in H and Cc, but not in Bs or C. The results also indicated strong correlations between DA and DOPAC, and SA and NE in all of the brain regions, and also between SA and 5-HT/HIAA in H and Cc. These results may indicate the contribution of biogenic amines, especially NE and 5-HT/HIAA to SA overproduction in some brain regions and may also indicate the potential of long term neurotoxic effects of those biogenic amines, in response to subchronic exposure to TCDD.
Figures


References
-
- Agostinelli E, Arancia G, Vedova LD, Belli F, Marra M, Salvi M, Toninello A. The biological functions of polyamine oxidation products by amine oxidases: perspectives of clinical applications. Amino Acids. 2004;27:347–358. - PubMed
-
- Alsharif NZ, Tang L, Hassoun E, Elmetwally T, Pederson C, Shara M, Stohs SJ. Role of oxidative stress in the chronic toxicity of TCDD in C57BL/6J female mice. The Toxicologist. 1999;48:218.
-
- Auger J, Boulay R, Jaillais B, delion-Vancassel S. analysis of biogenic amines by solid phase microextraction and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with electrochemical detection. J Chromatography. 2000;870:395–403. - PubMed
-
- Cadenas E, Davies KJ. Mitochondrial free radical generation, oxidative stress and aging. Free Rad Biol Med. 2000;29:222–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

