Inhibition of tumor endothelial ERK activation, angiogenesis, and tumor growth by sorafenib (BAY43-9006)
- PMID: 17071608
- PMCID: PMC1780219
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.050711
Inhibition of tumor endothelial ERK activation, angiogenesis, and tumor growth by sorafenib (BAY43-9006)
Abstract
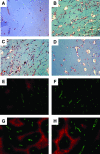
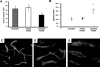
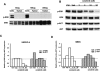
Activation of the Raf-MEK-ERK signal transduction pathway in endothelial cells is required for angiogenesis. Raf is the kinase most efficiently inhibited by the multikinase inhibitor sorafenib, which has shown activity against certain human cancers in clinical trials. To understand the mechanisms underlying this activity, we studied how it controlled growth of K1735 murine melanomas. Therapy caused massive regional tumor cell death accompanied by severe tumor hypoxia, decreased microvessel density, increased percentage of pericyte-covered vessels, and increased caliber and decreased arborization of vessels. These signs of K1735 angiogenesis inhibition, along with its ability to inhibit Matrigel neovascularization, showed that sorafenib is an effective anti-angiogenic agent. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation in tumor endothelial cells, revealed by immunostaining for phospho-ERK and CD34, was inhibited, whereas AKT activation, revealed by phospho-AKT immunostaining, was not inhibited in K1735 and two other tumor types treated with sorafenib. Treatment decreased endothelial but not tumor cell proliferation and increased both endothelial cell and tumor cell apoptosis. These data indicate that sorafenib's anti-tumor efficacy may be primarily attributable to angiogenesis inhibition resulting from its inhibition of Raf-MEK-ERK signaling in endothelial cells. Assessing endothelial cell ERK activation in tumor bio-psies may provide mechanistic insights into and allow monitoring of sorafenib's activity in patients in clinical trials.
Figures
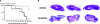


References
-
- Almoguera C, Shibata D, Forrester K, Martin J, Arnheim N, Perucho M. Most human carcinomas of the exocrine pancreas contain mutant c-K-ras genes. Cell. 1988;53:549–554. - PubMed
-
- Forrester K, Almoguera C, Han K, Grizzle WE, Perucho M. Detection of high incidence of K-ras oncogenes during human colon tumorigenesis. Nature. 1987;327:298–303. - PubMed
-
- Bos JL, Fearon ER, Hamilton SR, Verlaan-de Vries M, van Boom JH, van der Eb AJ, Vogelstein B. Prevalence of ras gene mutations in human colorectal cancers. Nature. 1987;327:293–297. - PubMed
-
- Bos JL. Ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 1989;49:4682–4689. - PubMed
-
- Brose MS, Volpe P, Feldman M, Kumar M, Rishi I, Gerrero R, Einhorn E, Herlyn M, Minna J, Nicholson A, Roth JA, Albelda SM, Davies H, Cox C, Brignell G, Stephens P, Futreal PA, Wooster R, Stratton MR, Weber BL. BRAF and RAS mutations in human lung cancer and melanoma. Cancer Res. 2002;62:6997–7000. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

