The RpoT regulon of Pseudomonas putida DOT-T1E and its role in stress endurance against solvents
- PMID: 17071759
- PMCID: PMC1797225
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00950-06
The RpoT regulon of Pseudomonas putida DOT-T1E and its role in stress endurance against solvents
Abstract
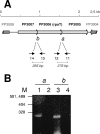
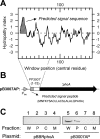
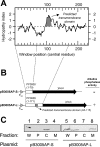
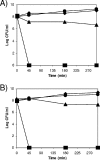
Pseudomonas putida encodes 20 extracytoplasmic sigma factors (ECFs). In this study, we show that one of these ECFs, known as ECF-Pp12 (PP3006), plays a role in tolerance of toluene and other organic solvents. Based on this finding, we have called the gene that encodes this new ECF rpoT. The rpoT gene forms an operon with the preceding gene and with the gene located downstream. The translated gene product of the open reading frame PP3005 is an inner membrane protein, whereas the PP3007 protein is periplasmic. A nonpolar DeltarpoT mutant was generated by homologous recombination, and survival of the mutant was tested under various stress conditions. The mutant strain was hypersensitive to toluene and other solvents but just as tolerant as the wild type of stress imposed by heat, antibiotics, NaCl, paraquat, sodium dodecyl sulfate, H(2)O(2), and benzoate. In the DeltarpoT mutant background, expression of around 50 transcriptional units was affected: 31 cistrons were upregulated, and 23 cistrons were downregulated. This indicates that about 1% of all P. putida genes are under the direct or indirect influence of RpoT. The rpoT gene controls the expression of a number of membrane proteins, including components of the respiratory chains, porins, transporters, and multidrug efflux pumps. Hypersensitivity of the P. putida RpoT-deficient mutant to organic solvents can be attributed to the fact that in the DeltarpoT strain, expression of the toluene efflux pump ttgGHI genes is severalfold lower than in the parental strain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The ttgGHI solvent efflux pump operon of Pseudomonas putida DOT-T1E is located on a large self-transmissible plasmid.Environ Microbiol. 2007 Jun;9(6):1550-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01276.x. Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17504492
-
Mutations in genes involved in the flagellar export apparatus of the solvent-tolerant Pseudomonas putida DOT-T1E strain impair motility and lead to hypersensitivity to toluene shocks.J Bacteriol. 2001 Jul;183(14):4127-33. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.14.4127-4133.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11418551 Free PMC article.
-
Global and cognate regulators control the expression of the organic solvent efflux pumps TtgABC and TtgDEF of Pseudomonas putida.Mol Microbiol. 2001 Feb;39(4):1100-6. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02310.x. Mol Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11251828
-
Mechanisms of solvent tolerance in gram-negative bacteria.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2002;56:743-68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.56.012302.161038. Epub 2002 Jan 30. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12142492 Review.
-
Analysis of solvent tolerance in Pseudomonas putida DOT-T1E based on its genome sequence and a collection of mutants.FEBS Lett. 2012 Aug 31;586(18):2932-8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.07.031. Epub 2012 Jul 20. FEBS Lett. 2012. PMID: 22819823 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of resistance to chloramphenicol in Pseudomonas putida KT2440.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Feb;56(2):1001-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05398-11. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22143519 Free PMC article.
-
A set of activators and repressors control peripheral glucose pathways in Pseudomonas putida to yield a common central intermediate.J Bacteriol. 2008 Apr;190(7):2331-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.01726-07. Epub 2008 Feb 1. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18245293 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial responses to xenobiotic compounds. Identification of genes that allow Pseudomonas putida KT2440 to cope with 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene.Microb Biotechnol. 2009 Mar;2(2):287-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7915.2009.00085.x. Microb Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 21261922 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of five ECF sigma factors in the genome of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae B728a.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58846. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058846. Epub 2013 Mar 14. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23516563 Free PMC article.
-
CsbD, a Novel Group B Streptococcal Stress Response Factor That Contributes to Bacterial Resistance against Environmental Bile Salts.J Bacteriol. 2023 Jun 27;205(6):e0044822. doi: 10.1128/jb.00448-22. Epub 2023 May 17. J Bacteriol. 2023. PMID: 37195202 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bendtsen, J. D., H. Nielsen, G. von Heijne, and S. Brunak. 2004. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J. Mol. Biol. 340:783-795. - PubMed
-
- Brazma, A., P. Hingamp, J. Quackenbush, G. Sherlock, P. Spellman, C. Stoeckert, J. Aach, W. Ansorge, C. A. Ball, H. C. Causton, T. Gaasterland, P. Glenisson, F. C. P. Holstege, I. F. Kim, V. Markowitz, J. C. Matese, H. Parkinson, A. Robinson, U. Sarkans, S. Schulze-Kremer, J. Stewart, R. Taylor, J. Vilo, and M. Vingron. 2001. Minimum information about a microarray experiment (MIAME)—towards standards for microarray data. Nat. Genet. 29:365-371. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

