Isolation and identification of a Paenibacillus polymyxa strain that coproduces a novel lantibiotic and polymyxin
- PMID: 17071789
- PMCID: PMC1797129
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02023-06
Isolation and identification of a Paenibacillus polymyxa strain that coproduces a novel lantibiotic and polymyxin
Abstract
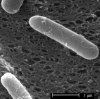
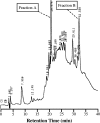
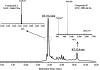
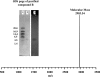
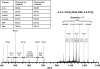
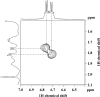
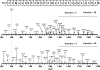
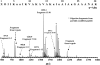
A new bacterial strain, displaying potent antimicrobial properties against gram-negative and gram-positive pathogenic bacteria, was isolated from food. Based on its phenotypical and biochemical properties as well as its 16S rRNA gene sequence, the bacterium was identified as Paenibacillus polymyxa and it was designated as strain OSY-DF. The antimicrobials produced by this strain were isolated from the fermentation broth and subsequently analyzed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Two antimicrobials were found: a known antibiotic, polymyxin E1, which is active against gram-negative bacteria, and an unknown 2,983-Da compound showing activity against gram-positive bacteria. The latter was purified to homogeneity, and its antimicrobial potency and proteinaceous nature were confirmed. The antimicrobial peptide, designated paenibacillin, is active against a broad range of food-borne pathogenic and spoilage bacteria, including Bacillus spp., Clostridium sporogenes, Lactobacillus spp., Lactococcus lactis, Leuconostoc mesenteroides, Listeria spp., Pediococcus cerevisiae, Staphylococcus aureus, and Streptococcus agalactiae. Furthermore, it possesses the physico-chemical properties of an ideal antimicrobial agent in terms of water solubility, thermal resistance, and stability against acid/alkali (pH 2.0 to 9.0) treatment. Edman degradation, mass spectroscopy, and nuclear magnetic resonance were used to sequence native and chemically modified paenibacillin. While details of the tentative sequence need to be elucidated in future work, the peptide was unequivocally characterized as a novel lantibiotic, with a high degree of posttranslational modifications. The coproduction of polymyxin E1 and a lantibiotic is a finding that has not been reported earlier. The new strain and associated peptide are potentially useful in food and medical applications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Draft genome sequence of Paenibacillus polymyxa OSY-DF, which coproduces a lantibiotic, paenibacillin, and polymyxin E1.J Bacteriol. 2012 Sep;194(17):4739-40. doi: 10.1128/JB.00846-12. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22887654 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of a protective bacterial culture isolated from honey active against American Foulbrood disease.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009 Jul;296(1):39-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01615.x. Epub 2009 Apr 15. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009. PMID: 19459943
-
Identification of a novel two-peptide lantibiotic, haloduracin, produced by the alkaliphile Bacillus halodurans C-125.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007 Feb;267(1):64-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00539.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007. PMID: 17233677
-
Reutericyclin: biological activity, mode of action, and potential applications.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2004 Apr;64(3):326-32. doi: 10.1007/s00253-003-1536-8. Epub 2004 Jan 21. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2004. PMID: 14735324 Review.
-
Bacteriocin production by Bifidobacterium spp. A review.Biotechnol Adv. 2013 Jul-Aug;31(4):482-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.01.010. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Biotechnol Adv. 2013. PMID: 23384878 Review.
Cited by
-
ApnI, a transmembrane protein responsible for subtilomycin immunity, unveils a novel model for lantibiotic immunity.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014 Oct;80(20):6303-15. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02280-14. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25085495 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Peptides: Opportunities for the Prevention and Treatment of Dental Caries.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2011 Jun;3(2):68. doi: 10.1007/s12602-011-9076-5. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2011. PMID: 26781572
-
Mycoidesin, a novel lantibiotic, exhibits potent bacteriostatic activity against Listeria monocytogenes and effectively controls its growth in beef.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025 Apr 23;91(4):e0006725. doi: 10.1128/aem.00067-25. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40130839 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond Soil-Dwelling Actinobacteria: Fantastic Antibiotics and Where to Find Them.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Feb 2;11(2):195. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11020195. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35203798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissection of Paenibacillus polymyxa NSY50-Induced Defense in Cucumber Roots against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cucumerinum by Target Metabolite Profiling.Biology (Basel). 2022 Jul 8;11(7):1028. doi: 10.3390/biology11071028. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36101409 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amabile-Cuevas, C. F. 2003. New antibiotics and new resistance. Am. Sci. 91:138-149.
-
- Berlana, D., J. M. Llop, E. Fort, M. B. Badia, and R. Jodar. 2005. Use of colistin in the treatment of multiple-drug-resistant gram-negative infections. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 62:39-47. - PubMed
-
- Cavanagh, J., and M. Rance. 1990. Sensitivity improvement in isotropic mixing (TOCSY) experiments. J. Magn. Reson. 88:72-85.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2006. Preliminary FoodNet data on the incidence of infection with pathogens transmitted commonly through food: 10 States, United States, 2005. Morbid. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 55:392-395. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

