Phospholamban and its phosphorylated form interact differently with lipid bilayers: a 31P, 2H, and 13C solid-state NMR spectroscopic study
- PMID: 17073452
- PMCID: PMC2586141
- DOI: 10.1021/bi0614028
Phospholamban and its phosphorylated form interact differently with lipid bilayers: a 31P, 2H, and 13C solid-state NMR spectroscopic study
Abstract
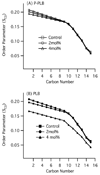
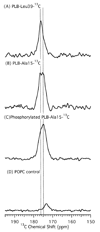
Phospholamban (PLB) is a 52-amino acid integral membrane protein that helps to regulate the flow of Ca(2+) ions in cardiac muscle cells. Recent structural studies on the PLB pentamer and the functionally active monomer (AFA-PLB) debate whether its cytoplasmic domain, in either the phosphorylated or dephosphorylated states, is alpha-helical in structure as well as whether it associates with the lipid head groups (Oxenoid, K. (2005) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 10870-10875; Karim, C. B. (2004) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101, 14437-14442; Andronesi, C.A. (2005) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 12965-12974; Li, J. (2003) Biochemistry 42, 10674-10682; Metcalfe, E. E. (2005) Biochemistry 44, 4386-4396: Clayton, J. C. (2005) Biochemistry 44, 17016-17026). Comparing the secondary structure of the PLB pentamer and its phosphorylated form (P-PLB) as well as their interaction with the lipid bilayer is crucial in order to understand its regulatory function. Therefore, in this study, the full-length wild-type (WT) PLB and P-PLB were incorporated into 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-phosphocholine (POPC) phospholipid bilayers and studied utilizing solid-state NMR spectroscopy. The analysis of the (2)H and (31)P solid-state NMR data of PLB and P-PLB in POPC multilamellar vesicles (MLVs) indicates that a direct interaction takes place between both proteins and the phospholipid head groups. However, the interaction of P-PLB with POPC bilayers was less significant compared that with PLB. Moreover, the secondary structure using (13)C=O site-specific isotopically labeled Ala15-PLB and Ala15-P-PLB in POPC bilayers suggests that this residue, located in the cytoplasmic domain, is a part of an alpha-helical structure for both PLB and P-PLB.
Figures




References
-
- Arora A, Abildgaard F, Bushweller JH, Tamm LK. NMR solution structure and dynamics of the outer membrane protein A ransmembrane domain in dodecylphosphocholine micelles. Biophys. J. 2002;82:516A–516A.
-
- Biverstahl H, Andersson A, Graslund A, Maler L. NMR solution structure and membrane interaction of the N-terminal sequence (1–30) of the bovine prion protein. Biochemistry. 2004;43:14940–14947. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez C, Wuthrich K. NMR solution structure determination of membrane proteins reconstituted in detergent micelles. FEBS Lett. 2003;555:144–150. - PubMed
-
- Haugen HS, Fimland G, Nissen-Meyer J, Kristiansen PE. Three-dimensional structure in lipid micelles of the pediocin-like antimicrobial peptide curvacin A. Biochemistry. 2005;44:16149–16157. - PubMed
-
- Marcinowski KJ, Shao H, Clancy EL, Zagorski MG. Solution structure model of residues 1–28 of the amyloid beta peptide when bound to micelles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998;120:11082–11091.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

