The quorum-quenching metallo-gamma-lactonase from Bacillus thuringiensis exhibits a leaving group thio effect
- PMID: 17073460
- PMCID: PMC2526230
- DOI: 10.1021/bi061238o
The quorum-quenching metallo-gamma-lactonase from Bacillus thuringiensis exhibits a leaving group thio effect
Abstract
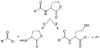
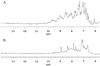
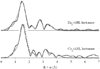
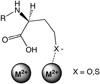
Lactone-hydrolyzing enzymes derived from some Bacillus species are capable of disrupting quorum sensing in bacteria that use N-acyl-l-homoserine lactones (AHLs) as intercellular signaling molecules. Despite the promise of these quorum-quenching enzymes as therapeutic and anti-biofouling agents, the ring opening mechanism and the role of metal ions in catalysis have not been elucidated. Labeling studies using (18)O, (2)H, and the AHL lactonase from Bacillus thuringiensis implicate an addition-elimination pathway for ring opening in which a solvent-derived oxygen is incorporated into the product carboxylate, identifying the alcohol as the leaving group. (1)H NMR is used to show that metal binding is required to maintain proper folding. A thio effect is measured for hydrolysis of N-hexanoyl-l-homoserine lactone and the corresponding thiolactone by AHL lactonase disubstituted with alternative metal ions, including Mn(2+), Co(2+), Zn(2+), and Cd(2+). The magnitude of the thio effect on k(cat) values and the thiophilicity of the metal ion substitutions vary in parallel and are consistent with a kinetically significant interaction between the leaving group and the active site metal center during turnover. X-ray absorption spectroscopy confirms that dicobalt substitution does not result in large structural perturbations at the active site. Finally, substitution of the dinuclear metal site with Cd(2+) results in a greatly enhanced catalyst that can hydrolyze AHLs 1600-24000-fold faster than other reported quorum-quenching enzymes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A phenylalanine clamp controls substrate specificity in the quorum-quenching metallo-γ-lactonase from Bacillus thuringiensis.Biochemistry. 2013 Mar 5;52(9):1603-10. doi: 10.1021/bi400050j. Epub 2013 Feb 20. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23387521 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of the quorum-quenching lactonase (AiiA) from Bacillus thuringiensis. 1. Product-bound structures.Biochemistry. 2008 Jul 22;47(29):7706-14. doi: 10.1021/bi800368y. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18627129 Free PMC article.
-
The quorum-quenching lactonase from Bacillus thuringiensis is a metalloprotein.Biochemistry. 2005 May 24;44(20):7559-69. doi: 10.1021/bi050050m. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15895999
-
Novel roles of Bacillus thuringiensis to control plant diseases.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008 Sep;80(4):563-72. doi: 10.1007/s00253-008-1610-3. Epub 2008 Jul 25. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 18654770 Review.
-
Quenching of acyl-homoserine lactone-dependent quorum sensing by enzymatic disruption of signal molecules.Acta Biochim Pol. 2009;56(1):1-16. Epub 2009 Mar 17. Acta Biochim Pol. 2009. PMID: 19287806 Review.
Cited by
-
A phenylalanine clamp controls substrate specificity in the quorum-quenching metallo-γ-lactonase from Bacillus thuringiensis.Biochemistry. 2013 Mar 5;52(9):1603-10. doi: 10.1021/bi400050j. Epub 2013 Feb 20. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23387521 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of the quorum-quenching lactonase (AiiA) from Bacillus thuringiensis. 2. Substrate modeling and active site mutations.Biochemistry. 2008 Jul 22;47(29):7715-25. doi: 10.1021/bi8003704. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18627130 Free PMC article.
-
Catalytic Redundancies and Conformational Plasticity Drives Selectivity and Promiscuity in Quorum Quenching Lactonases.JACS Au. 2024 Aug 23;4(9):3519-3536. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.4c00404. eCollection 2024 Sep 23. JACS Au. 2024. PMID: 39328773 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing Antibiotic-Resistant Microbe Combat: Nanocarrier-Based Systems in Combination Therapy Targeting Quorum Sensing.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Sep 3;16(9):1160. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16091160. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39339197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization and complete sequence of lactonase enzyme from Bacillus weihenstephanensis isolate P65 with potential activity against acyl homoserine lactone signal molecules.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:192589. doi: 10.1155/2013/192589. Epub 2013 Jul 9. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23936779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singh PK, Schaefer AL, Parsek MR, Moninger TO, Welsh MJ, Greenberg EP. Quorum-sensing signals indicate that cystic fibrosis lungs are infected with bacterial biofilms. Nature. 2000;407:762–4. - PubMed
-
- Smith RS, Iglewski BH. P. aeruginosa quorum-sensing systems and virulence. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003;6:56–60. - PubMed
-
- Lewenza S, Visser MB, Sokol PA. Interspecies communication between Burkholderia cepacia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can. J. Microbiol. 2002;48:707–16. - PubMed
-
- Dong YH, Zhang LH. Quorum sensing and quorum-quenching enzymes. J. Microbiol. 2005;43:101–9. - PubMed
-
- Rice SA, McDougald D, Kumar N, Kjelleberg S. The use of quorum-sensing blockers as therapeutic agents for the control of biofilm-associated infections. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2005;6:178–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

