Circulating levels of adiponectin in preterm infants
- PMID: 17074785
- PMCID: PMC2675429
- DOI: 10.1136/adc.2006.106112
Circulating levels of adiponectin in preterm infants
Abstract
Objective: To determine circulating levels of adiponectin in preterm infants and examine possible associations with anthropometric measurements, weight gain, and leptin and insulin levels.
Design: Prospective study.
Setting: A university hospital neonatal care unit.
Study population: 62 preterm (mean (SD) gestational age 32.0 (2.1) weeks) and 15 full-term infants (reference group).
Interventions: Blood samples taken at discharge (40.9 (14.8) days of life) from the preterm infants and at a comparable postnatal age in full-term infants. All infants were fed the same commercial formula, but in nine preterms the formula contained long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LCPUFAs).
Main outcome measures: Serum levels of adiponectin, leptin and insulin. Associations of adiponectin levels were tested only in the preterm group.
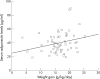
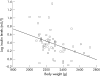
Results: Serum levels of adiponectin were lower in preterm (40.9 (14.8) microg/ml) than full-term infants (53.1 (16.0) microg/ml, p<0.01). However, after adjustment for body weight, the influence of prematurity on adiponectin levels was no longer significant. In preterm infants, adiponectin levels independently correlated with being born small for gestational age (SGA) (beta=-0.35, p=0.01), weight gain (beta=0.28, p=0.03) and LCPUFA-supplemented formula (beta=0.34, p=0.009). Serum adiponectin levels did not correlate with insulin or leptin levels. However, insulin levels were higher in preterm than in full-term infants after adjustment for body weight.
Conclusions: Adiponectin levels are lower in preterm infants at discharge than full-term infants probably due to decreased adiposity. The levels are influenced by being born SGA, weight gain and, possibly, by dietary LCPUFAs. The importance of these findings in the development of insulin or leptin resistance in children born prematurely needs to be further studied.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
References
-
- Das U N. Pathophysiology of metabolic syndrome X and its links to the perinatal period. Nutrition 200521762–773. - PubMed
-
- Barker D J P, Osmond C, Forsen T J.et al Trajectories of growth among children who have coronary events as adults. N Engl J Med 20053531802–1809. - PubMed
-
- Singhal A, Lucas A. Early origins of cardiovascular disease: is there a unifying hypothesis? Lancet 20043631642–1645. - PubMed
-
- Hofman P L, Regan F, Jackson W E.et al Premature birth and later insulin resistance. N Engl J Med 20043512179–2186. - PubMed
-
- Nedvidkova J, Smitka K, Kopsky V.et al Adiponectin, an adipocyte‐derived protein. Physiol Res 200554133–140. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical