A cooperative action of the ATP-dependent import motor complex and the inner membrane potential drives mitochondrial preprotein import
- PMID: 17074805
- PMCID: PMC1800818
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01391-06
A cooperative action of the ATP-dependent import motor complex and the inner membrane potential drives mitochondrial preprotein import
Abstract
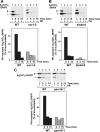
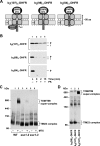
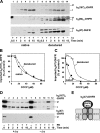
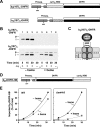
The import of mitochondrial preproteins requires an electric potential across the inner membrane and the hydrolysis of ATP in the matrix. We assessed the contributions of the two energy sources to the translocation driving force responsible for movement of the polypeptide chain through the translocation channel and the unfolding of preprotein domains. The import-driving activity was directly analyzed by the determination of the protease resistances of saturating amounts of membrane-spanning translocation intermediates. The ability to generate a strong translocation-driving force was solely dependent on the activity of the ATP-dependent import motor complex in the matrix. For a sustained import-driving activity on the preprotein in transit, an unstructured N-terminal segment of more than 70 to 80 amino acid residues was required. The electric potential of the inner membrane was required to maintain the import-driving activity at a high level. The electrophoretic force of the potential exhibited only a limited capacity to unfold preprotein domains. We conclude that the membrane potential increases the probability of a dynamic interaction of the preprotein with the import motor. Polypeptide translocation and unfolding are mainly driven by the inward-directed translocation activity based on the functional cooperation of the import motor components.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Motor-free mitochondrial presequence translocase drives membrane integration of preproteins.Nat Cell Biol. 2007 Oct;9(10):1152-9. doi: 10.1038/ncb1635. Epub 2007 Sep 9. Nat Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17828250
-
Unfolding of preproteins upon import into mitochondria.EMBO J. 1998 Nov 16;17(22):6497-507. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.22.6497. EMBO J. 1998. PMID: 9822595 Free PMC article.
-
The mitochondrial Hsp70-dependent import system actively unfolds preproteins and shortens the lag phase of translocation.EMBO J. 2001 Mar 1;20(5):941-50. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.5.941. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11230118 Free PMC article.
-
The mitochondrial protein import motor.Biol Chem. 2000 Sep-Oct;381(9-10):943-9. doi: 10.1515/BC.2000.115. Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 11076025 Review.
-
Mitochondrial preprotein translocases as dynamic molecular machines.FEMS Yeast Res. 2006 Sep;6(6):849-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1567-1364.2006.00134.x. FEMS Yeast Res. 2006. PMID: 16911507 Review.
Cited by
-
Distinct forms of mitochondrial TOM-TIM supercomplexes define signal-dependent states of preprotein sorting.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Jan;30(1):307-18. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00749-09. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 19884344 Free PMC article.
-
Sorting switch of mitochondrial presequence translocase involves coupling of motor module to respiratory chain.J Cell Biol. 2007 Dec 17;179(6):1115-22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200709087. Epub 2007 Dec 10. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 18070913 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple pathways for sorting mitochondrial precursor proteins.EMBO Rep. 2008 Jan;9(1):42-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7401126. EMBO Rep. 2008. PMID: 18174896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial protein import and the genesis of steroidogenic mitochondria.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011 Apr 10;336(1-2):70-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2010.12.007. Epub 2010 Dec 13. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21147195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Residues of Tim44 involved in both association with the translocon of the inner mitochondrial membrane and regulation of mitochondrial Hsp70 tethering.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Jul;28(13):4424-33. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00007-08. Epub 2008 Apr 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18426906 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bauer, M. F., S. Hofmann, W. Neupert, and M. Brunner. 2000. Protein translocation into mitochondria: the role of TIM complexes. Trends Cell Biol. 10:25-31. - PubMed
-
- Bauer, M. F., C. Sirrenberg, W. Neupert, and M. Brunner. 1996. Role of Tim23 as voltage sensor and presequence receptor in protein import into mitochondria. Cell 87:33-41. - PubMed
-
- Bömer, U., A. C. Maarse, F. Martin, A. Geissler, A. Merlin, B. Schönfisch, M. Meijer, N. Pfanner, and J. Rassow. 1998. Separation of structural and dynamic functions of the mitochondrial translocase: Tim44 is crucial for the inner membrane import sites in translocation of tightly folded domains, but not of loosely folded preproteins. EMBO J. 17:4226-4237. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
