Time to renal disease and end-stage renal disease in PROFILE: a multiethnic lupus cohort
- PMID: 17076550
- PMCID: PMC1626549
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030396
Time to renal disease and end-stage renal disease in PROFILE: a multiethnic lupus cohort
Abstract
Background: Renal involvement is a serious manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE); it may portend a poor prognosis as it may lead to end-stage renal disease (ESRD). The purpose of this study was to determine the factors predicting the development of renal involvement and its progression to ESRD in a multi-ethnic SLE cohort (PROFILE).
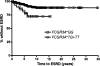
Methods and findings: PROFILE includes SLE patients from five different United States institutions. We examined at baseline the socioeconomic-demographic, clinical, and genetic variables associated with the development of renal involvement and its progression to ESRD by univariable and multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression analyses. Analyses of onset of renal involvement included only patients with renal involvement after SLE diagnosis (n = 229). Analyses of ESRD included all patients, regardless of whether renal involvement occurred before, at, or after SLE diagnosis (34 of 438 patients). In addition, we performed a multivariable logistic regression analysis of the variables associated with the development of renal involvement at any time during the course of SLE. In the time-dependent multivariable analysis, patients developing renal involvement were more likely to have more American College of Rheumatology criteria for SLE, and to be younger, hypertensive, and of African-American or Hispanic (from Texas) ethnicity. Alternative regression models were consistent with these results. In addition to greater accrued disease damage (renal damage excluded), younger age, and Hispanic ethnicity (from Texas), homozygosity for the valine allele of FcgammaRIIIa (FCGR3A*GG) was a significant predictor of ESRD. Results from the multivariable logistic regression model that included all cases of renal involvement were consistent with those from the Cox model.
Conclusions: Fcgamma receptor genotype is a risk factor for progression of renal disease to ESRD. Since the frequency distribution of FCGR3A alleles does not vary significantly among the ethnic groups studied, the additional factors underlying the ethnic disparities in renal disease progression remain to be elucidated.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ward MM, Studenski S. Clinical prognostic factors in lupus nephritis. The importance of hypertension and smoking. Arch Intern Med. 1992;152:2082–2088. - PubMed
-
- Stewart M, Petri M. Lupus nephritis outcomes: Health maintenance organizations compared to non-health maintenance organizations. J Rheumatol. 2000;27:900–902. - PubMed
-
- Kimberly RP, Lockshin MD, Sherman RL, Beary JF, Mouradian T, et al. “End-stage” lupus nephritis: Clinical course to and outcome on dialysis. Experience with 39 patients. Medicine. 1981;60:277–287. - PubMed
-
- Petri M, Perez-Gutthann S, Longenecker JC, Hochberg M. Morbidity of systemic lupus erythematosus: Role of race and socioeconomic status. Am J Med. 1991;91:345–353. - PubMed
-
- Petri M. The effect of race on incidence and clinical course in systemic lupus erythematosus: The Hopkins Lupus Cohort. J Am Med Womens Assoc. 1998;53:9–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K24-AR002138/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01AR49084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR02558/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR011126/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 1P20-RR11126/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000048/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00048/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR42503/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR048098/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR02558/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P60AR048098/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043727/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR002558/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000032/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AR002138/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042503/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR43727/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AR049084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00032/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical