Leptin: a diverse regulator of neuronal function
- PMID: 17076761
- PMCID: PMC1781059
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04205.x
Leptin: a diverse regulator of neuronal function
Abstract
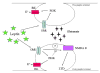
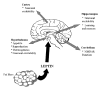
It is well documented that leptin is a circulating hormone that plays a key role in regulating food intake and body weight via its actions on specific hypothalamic nuclei. However, leptin receptors are widely expressed in the CNS, in regions not generally associated with energy homeostasis, such as the hippocampus, cortex and cerebellum. Moreover, evidence is accumulating that leptin has widespread actions in the brain. In particular, recent studies have demonstrated that leptin markedly influences the excitability of hippocampal neurons via its ability to activate large conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) (BK) channels, and also to promote long-term depression of excitatory synaptic transmission. Here, we review the evidence supporting a role for this hormone in regulating hippocampal excitability.
Figures
References
-
- Attoub S, Noe V, Pirola L, Bruyneel E, Chastre E, Mareel M, Wymann MP, Gespach C. Leptin promotes invasiveness of kidney and colonic epithelial cells via phosphoinositide 3-kinase-, rho-, and rac-dependent signaling pathways. FASEB J. 2000;14:2329–38. - PubMed
-
- Ayyildiz M, Yildirim M, Agar E, Baltaci AK. The effect of leptin on penicillin-induced epileptiform-like activity in rats. Brain Res Bull. 2006;68:374–378. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA. Enhanced leptin transport across the blood brain barrier by alpha 1-adrenergic agents. Brain Res. 2001;899:209–17. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Clever CM, Farrell CL. Partial saturation and regional variation in the blood-to-brain transport of leptin in normal weight mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2000;278:E1158–65. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Coon AB, Robinson SM, Moinuddin A, Shultz JM, Nakaoke R, Morley JE. Triglycerides induce leptin resistance at the blood brain barrier. Diabetes. 2004;53:1253–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

