Human ACE and bradykinin B2 receptors form a complex at the plasma membrane
- PMID: 17077303
- PMCID: PMC1635968
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.06-6113com
Human ACE and bradykinin B2 receptors form a complex at the plasma membrane
Abstract
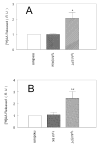
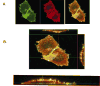
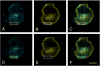
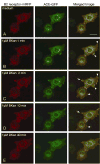
To investigate how angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors enhance the actions of bradykinin (BK) on B2 receptors independent of blocking BK inactivation, we expressed human somatic ACE and B2 receptors in CHO cells. Bradykinin and its ACE-resistant analog were the receptor agonists. B2 fused with green fluorescent protein (GFP) and ACE were coprecipitated with antisera to GFP or ACE shown in Western blots. Immunohistochemistry of fixed cells localized ACE by red color and B2-GFP by green. Yellow on plasma membranes of coexpressing cells also indicated enzyme-receptor complex formation. Using ACE-fused cyan fluorescent protein donor and B2-fused yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) acceptor, we registered fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) by the enhanced fluorescence of donor on acceptor photobleaching, establishing close (within 10 nm) positions of B2 receptors and ACE. Bradykinin stimulation cointernalized ACE and B2 receptors. We expressed ACE fused to N terminus of B2 receptors, anchoring only receptors to plasma membranes. Here, in contrast to cells, where both ACE and B2 receptors are separately anchored, ACE inhibitors neither enhance activation of chimeric B2 nor resensitize desensitized B2 receptors. Heterodimer formation between ACE and B2 receptors can be a mechanism for ACE inhibitors to augment kinin activity at cellular level.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hydrolysis of angiotensin peptides by human angiotensin I-converting enzyme and the resensitization of B2 kinin receptors.Hypertension. 2005 Dec;46(6):1368-73. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000188905.20884.63. Epub 2005 Oct 24. Hypertension. 2005. PMID: 16246972 Free PMC article.
-
Replacement of the transmembrane anchor in angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) with a glycosylphosphatidylinositol tail affects activation of the B2 bradykinin receptor by ACE inhibitors.J Biol Chem. 2000 May 26;275(21):16110-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M909490199. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10748135
-
ACE activity is modulated by kinin B2 receptor.Hypertension. 2008 Mar;51(3):689-95. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.091181. Epub 2008 Jan 22. Hypertension. 2008. PMID: 18212275
-
[ACE inhibitors--activators of kinin receptors].Biomed Khim. 2011 May-Jun;57(3):282-99. Biomed Khim. 2011. PMID: 21863742 Review. Russian.
-
Kinins, receptors, kininases and inhibitors--where did they lead us?Biol Chem. 2001 Jan;382(1):43-7. doi: 10.1515/BC.2001.007. Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11258670 Review.
Cited by
-
A new role for PTEN in regulating transient receptor potential canonical channel 6-mediated Ca2+ entry, endothelial permeability, and angiogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 22;285(43):33082-33091. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.142034. Epub 2010 Aug 12. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20705603 Free PMC article.
-
Carboxypeptidase M augments kinin B1 receptor signaling by conformational crosstalk and enhances endothelial nitric oxide output.Biol Chem. 2013 Mar;394(3):335-45. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2012-0290. Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23183746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The SARS-CoV-2/Receptor Axis in Heart and Blood Vessels: A Crisp Update on COVID-19 Disease with Cardiovascular Complications.Viruses. 2021 Jul 12;13(7):1346. doi: 10.3390/v13071346. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34372552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scavenger receptor class B, type I (SR-BI) homo-dimerizes via its C-terminal region: fluorescence resonance energy transfer analysis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Jul;1771(7):818-29. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2007.04.019. Epub 2007 May 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17556017 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of kinin B1 receptor function by B2 receptor heterodimerization and signaling.Cell Signal. 2015 Jan;27(1):90-103. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.09.019. Epub 2014 Oct 5. Cell Signal. 2015. PMID: 25289859 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Webster, M. E. (1970) Kallikreins in glandular tissues. In Bradykinin, Kallidin and Kallikrein. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. (Erdös, E. G., ed) Vol. XXV pp. 131–155, Springer Verlag, Heidelberg
-
- Werle E. Discovery of the most important kallikreins and kallikrein inhibitors. In: Erdös EG, editor. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. XXV. Springer-Verlag; Heidelberg: 1970. pp. 1–6.
-
- Beraldo WT, Andrade SP. Discovery of bradykinin and the kallikrein-kinin system. In: Farmer SG, editor. The Kinin System. Academic Press Ltd.; San Diego, CA: 1997. pp. 1–8.
-
- Page IH. Hypertension Research. A Memoir 1920–1960. Pergamon Press; New York: 1988. pp. 1–167.
-
- Yang HYT, Erdös EG. Second kininase in human blood plasma. Nature. 1967;215:1402–1403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

