Connection, regulation, and care plan innovation: a case study of four nursing homes
- PMID: 17077708
- PMCID: PMC1952654
- DOI: 10.1097/00004010-200610000-00009
Connection, regulation, and care plan innovation: a case study of four nursing homes
Abstract
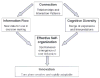
We describe how connections among nursing home staff impact the care planning process using a complexity science framework. We completed six-month case studies of four nursing homes. Field observations (n = 274), shadowing encounters (n = 69), and in-depth interviews (n = 122) of 390 staff at all levels were conducted. Qualitative analysis produced a conceptual/thematic description and complexity science concepts were used to produce conceptual insights. We observed that greater levels of staff connection were associated with higher care plan specificity and innovation. Connection of the frontline nursing staff was crucial for (1) implementation of the formal care plan and (2) spontaneous informal care planning responsive to changing resident needs. Although regulations could theoretically improve cognitive diversity and information flow in care planning, we observed instances of regulatory oversight resulting in less specific care plans and abandonment of an effective care planning process. Interventions which improve staff connectedness may improve resident outcomes.
Figures

References
-
- Dellefield ME. Interdisciplinary care planning and the written care plan in nursing homes: a critical review. Gerontologist. 2006;46(1):128–33. - PubMed
-
- Hawes C, Mor V, Phillips CD, Fries BE, Morris JN, Steele-Friedlob E, et al. The OBRA-87 Nursing Home Regulations and Implementation of the Resident Assessment Instrument: Effects on Process Quality. Journal of the American Geriatric Society. 1997;45:977–85. - PubMed
-
- Hawes C, Morris J, Phillips C, Fries B, Murhpy K, Mor V. Development of the Nursing Home Resident Assessment Instrument (RAI) in the US. Age & Ageing. 1997;26(S2):19–26. - PubMed
-
- Morris JN, Hawes C, Fries BE, Phillips CD, Mor V, Katz S, et al. Designing the National Resident Assessment Instrument for Nursing Homes. Gerontologist. 1990;30:293–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

