Evaluation of an osmotic pump for microdialysis sampling in an awake and untethered rat
- PMID: 17079021
- PMCID: PMC1945051
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2006.09.014
Evaluation of an osmotic pump for microdialysis sampling in an awake and untethered rat
Abstract
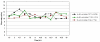
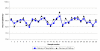
The feasibility of using an osmotic pump in place of a syringe pump for microdialysis sampling in rat brain was investigated. The use of an osmotic pump permits the rat to be free from the constraints of the standard tethered system. The in vitro flow rates of a microdialysis syringe pump (set at 10.80 microl/h) and the osmotic pump (pump specifications were 11.35 microl/h) with no probe attached were compared, yielding results of 10.87 microl/h+/-1.7% and 10.95 microl/h+/-8.0%, respectively. The average of four flow rate experiments in vivo yielded R.S.D.s less than 10% and an average flow rate of 11.1 microl/h. Following the flow rate studies, in vivo sampling of neurotransmitters was accomplished with the osmotic pump coupled to a microdialysis probe implanted in the brain. Finally, after determination of basal levels of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC), homovanillic acid (HVA), and 5-hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid (5-HIAA) in the rats, the rats were dosed with benserazide followed by l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (l-DOPA). The results from the dosing study showed at least a 10-fold increase in compounds in the l-DOPA metabolic pathway (DOPAC and HVA) and a slight or no increase in 5-HIAA (serotonin metabolic pathway.) These results indicate that the osmotic pump is a viable alternative to the syringe pump for use in microdialysis sampling.
Figures




Similar articles
-
In vivo on-line HPLC-microdialysis: simultaneous detection of monoamines and their metabolites in awake freely-moving rats.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1999 Mar;19(3-4):413-22. doi: 10.1016/s0731-7085(98)00182-4. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1999. PMID: 10704106
-
High-sensitive liquid chromatographic method for determination of neuronal release of serotonin, noradrenaline and dopamine monitored by microdialysis in the rat prefrontal cortex.J Neurosci Methods. 2004 Dec 30;140(1-2):163-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2004.04.041. J Neurosci Methods. 2004. PMID: 15589346
-
High temporal resolution for in vivo monitoring of neurotransmitters in awake epileptic rats using brain microdialysis and capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection.J Neurosci Methods. 2004 Dec 30;140(1-2):29-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2004.03.025. J Neurosci Methods. 2004. PMID: 15589331
-
Microdialysis applications in neuroscience.Neurol Res. 2008 Sep;30(7):661-8. doi: 10.1179/174313208X289570. Epub 2008 Jul 15. Neurol Res. 2008. PMID: 18631429 Review.
-
Emerging trends in in vivo neurochemical monitoring by microdialysis.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2013 Oct;17(5):860-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2013.06.012. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23856056 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of an on-animal separation-based sensor for monitoring drug metabolism in freely roaming sheep.Analyst. 2015 Jun 7;140(11):3820-9. doi: 10.1039/c4an01928h. Analyst. 2015. PMID: 25697221 Free PMC article.
-
PDMS/glass hybrid device with a reusable carbon electrode for on-line monitoring of catecholamines using microdialysis sampling coupled to microchip electrophoresis with electrochemical detection.Electrophoresis. 2018 Feb;39(3):462-469. doi: 10.1002/elps.201700211. Epub 2017 Aug 21. Electrophoresis. 2018. PMID: 28737835 Free PMC article.
-
Analytical and biological methods for probing the blood-brain barrier.Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2012;5:505-31. doi: 10.1146/annurev-anchem-062011-143002. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2012. PMID: 22708905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intraventricular Drug Delivery and Sampling for Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics Study.J Vis Exp. 2022 Mar 31;(181):10.3791/63540. doi: 10.3791/63540. J Vis Exp. 2022. PMID: 35435913 Free PMC article.
-
Microchip electrophoresis with electrochemical detection for the determination of analytes in the dopamine metabolic pathway.Electrophoresis. 2015 Aug;36(16):1912-9. doi: 10.1002/elps.201500150. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Electrophoresis. 2015. PMID: 25958983 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ALZET Pump Bibliography 2006. http://www.alzet.com/bibliography/agent.php.
-
- Bazzett T, Becker JB, Albin RL. Chronic intrastriatal administration of high and low dose quinolinic acid using a novel device for dialytic delivery. J Neurosci Methods. 1991;40:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Beagles KE, Morrison PF, Heyes MP. Quinolinic acid in vivo synthesis rates, extracellular concentrations, and intercompartmental distributions in normal and immune-activated brain as determined by multiple-isotope microdialysis. J Neurochem. 1998;70:281–91. - PubMed
-
- Cano-Cebrian MJ, Zornoza T, Polache A, Granero L. Quantitative microdialysis in pharmacokinetic studies: some reminders. Curr. Drug. Metab. 2005;6:83–90. - PubMed
-
- Cheng FC, Yang LL, Chang FM, Chia LG, Kuo JS. Simultaneous measurement of serotonin, catecholamines and their metabolites. J Chromatog. 1992;582:19–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

