High IgA rheumatoid factor levels are associated with poor clinical response to tumour necrosis factor alpha inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 17079248
- PMCID: PMC1856018
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.060608
High IgA rheumatoid factor levels are associated with poor clinical response to tumour necrosis factor alpha inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: To investigate whether rheumatoid factor isotypes and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies are related to clinical response in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) inhibitors.
Methods: The study was carried out on 132 patients with advanced rheumatoid arthritis refractory to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Patients were treated with infliximab (n = 63), etanercept (n = 35) or adalimumab (n = 34). All patients completed 1 year of follow-up, and 126 were evaluable for clinical response according to the disease activity score (DAS) criteria. IgM, IgA and IgG rheumatoid factors and anti-CCP antibodies were assessed by ELISA both before anti-TNFalpha treatment and 1 year later.
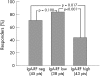
Results: The DAS response was reached in 66% of evaluable patients (61% infliximab, 65% etanercept and 76% adalimumab; p = 0.354). A significant reduction in the rheumatoid factor level was reported by all treatment groups after 1 year. The frequency of positive tests for the different antibodies did not differ between responders and non-responders at baseline; however, significantly higher IgA rheumatoid factor levels were reported by the non-responder group (130.4 U/ml (interquartile range 13.8-276.7) v 24.8 U/ml (10.2-90.8); p = 0.003). A significant decrease (p<0.001) in the levels of all rheumatoid factor isotypes in the responder group was reported after 1 year of treatment, whereas anti-CCP antibody levels were not significantly affected.
Conclusions: According to the clinical response, anti-TNFalpha agents seem to reduce IgM, IgG and IgA rheumatoid factor levels. More interestingly, high pretreatment levels of IgA rheumatoid factor are associated with a poor clinical response to TNFalpha inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Comment in
-
Do high levels of IgA rheumatoid factor indicate a poor response to treatment with TNF inhibitors in patients with RA?Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2007 Oct;3(10):544-5. doi: 10.1038/ncprheum0596. Epub 2007 Aug 28. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2007. PMID: 17726429 No abstract available.
References
-
- Johnson P M, Faulk W P. Rheumatoid factor: its nature, specificity, and production in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 19766414–430. - PubMed
-
- Swedler W, Wallman J, Froelich C J, Teodorescu M. Routine measurement of IgM, IgG, and IgA rheumatoid factors: high sensitivity, specificity, and predictive value for rheumatoid arthritis.J Rheumatol 1997241037–1044. - PubMed
-
- Zlabinger G J, Haberhauer G, Dax K, Menzel E J, Broll H. Rheumatoid factor isotypes and circulating immune complexes in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 19908113–119. - PubMed
-
- Jorgensen C, Legouffe M C, Bologna C, Brochier J, Sany J. IgA isotype rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid arthritis: clinical implications. Clin Exp Rheumatol 199614301–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous