Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 gene, a switch from latency to lytic infection, is expressed as an immediate-early gene after primary infection of B lymphocytes
- PMID: 17079287
- PMCID: PMC1797481
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01416-06
Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 gene, a switch from latency to lytic infection, is expressed as an immediate-early gene after primary infection of B lymphocytes
Abstract
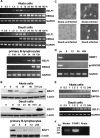
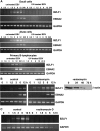
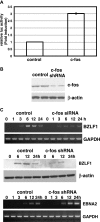
We demonstrate here that the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) BZLF1 gene, a switch from latent infection to lytic infection, is expressed as early as 1.5 h after EBV infection in Burkitt's lymphoma-derived, EBV-negative Akata and Daudi cells and primary B lymphocytes. Since BZLF1 mRNA is expressed even when the cells are infected with EBV in the presence of anisomycin, an inhibitor of protein synthesis, its expression does not require prerequisite protein synthesis, indicating that BZLF1 is expressed as an immediate-early gene following primary EBV infection of B lymphocytes.
Figures
References
-
- Alfieri, C., M. Birkenbach, and E. Kieff. 1991. Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection of human B lymphocytes. Virology 181:595-608. - PubMed
-
- Allday, M. J., D. H. Crawford, and B. E. Griffin. 1989. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression during the initiation of B-cell immortalization. J. Gen. Virol. 70:1755-1764. - PubMed
-
- Chen, H., J. M. Lee, Y. Wang, D. P. Huang, R. F. Ambinder, and S. D. Hayward. 1999. The Epstein-Barr virus latency BamHI-Q promoter is positively regulated by STATs and Zta interference with JAK/STAT activation leads to loss of BamHI-Q promoter activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96:9339-9344. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

