White spot syndrome virus annexes a shrimp STAT to enhance expression of the immediate-early gene ie1
- PMID: 17079306
- PMCID: PMC1797513
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01880-06
White spot syndrome virus annexes a shrimp STAT to enhance expression of the immediate-early gene ie1
Abstract
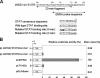
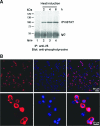
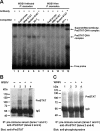
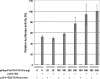
Although the Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK-STAT) signaling pathway is part of the antiviral response in arthropods such as Drosophila, here we show that white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) uses a shrimp STAT as a transcription factor to enhance viral gene expression in host cells. In a series of deletion and mutation assays using the WSSV immediate-early gene ie1 promoter, which is active in shrimp cells and also in insect Sf9 cells, an element containing a STAT binding motif was shown to be important for the overall level of WSSV ie1 promoter activity. In the Sf9 insect cell line, a specific protein-DNA complex was detected by using electrophoresis mobility shift assays (EMSA) with the 32P-labeled STAT binding motif of the WSSV ie1 promoter as the probe. When recombinant Penaeus monodon STAT (rPmSTAT) was overexpressed in Sf9 cells, EMSA with specific antibodies confirmed that the STAT was responsible for the formation of the specific protein-DNA complex. Another EMSA showed that in WSSV-infected P. monodon, levels of activated PmSTAT were higher than in WSSV-free P. monodon. A transactivation assay of the WSSV ie1 promoter demonstrated that increasing the level of rPmSTAT led to dose-dependent increases in ie1 promoter activity. These results show that STAT directly transactivates WSSV ie1 gene expression and contributes to its high promoter activity. We conclude that WSSV successfully annexes a putative shrimp defense mechanism, which it uses to enhance the expression of viral immediate-early genes.
Figures
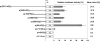
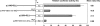
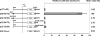


References
-
- Agaisse, H., and N. Perrimon. 2004. The roles of JAK/STAT signaling in Drosophila immune responses. Immunol. Rev. 198:72-82. - PubMed
-
- Agaisse, H., U. M. Petersen, M. Boutros, B. Mathey-Prevot, and N. Perrimon. 2003. Signaling role of hemocytes in Drosophila JAK/STAT-dependent response to septic injury. Dev. Cell. 5:441-450. - PubMed
-
- Akira, S., Y. Nishio, M. Inoue, X. J. Wang, S. Wei, T. Matsusaka, K. Yoshida, T. Sudo, M. Naruto, and T. Kishimoto. 1994. Molecular cloning of APRF, a novel IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 p91-related transcription factor involved in the gp130-mediated signaling pathway. Cell 77:63-71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

