Herpesvirus interference with major histocompatibility complex class II-restricted T-cell activation
- PMID: 17079308
- PMCID: PMC1900142
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01525-06
Herpesvirus interference with major histocompatibility complex class II-restricted T-cell activation
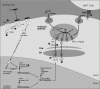
Figures
References
-
- Accolla, R. S., A. D. Barbaro, S. Mazza, C. Casoli, A. De Maria, and G. Tosi. 2001. The MHC class II transactivator: prey and hunter in infectious diseases. Trends Immunol. 22:560-563. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

