Dynamics of Helicobacter pylori-specific immunoglobulin G for 2 years after successful eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection in an American Indian and Alaska Native population
- PMID: 17079433
- PMCID: PMC1797704
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00253-06
Dynamics of Helicobacter pylori-specific immunoglobulin G for 2 years after successful eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection in an American Indian and Alaska Native population
Abstract
Helicobacter pylori antibodies were measured over 24 months in American Indian and Alaska Native persons who cleared their infections. Two months after treatment, 82% of H. pylori-negative persons remained seropositive. While there were declines in H. pylori antibodies for 12 months, after 24 months 71% of persons remained seropositive.
Figures
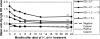
References
-
- Cutler, A. F., V. M. Prasad, and P. Santogade. 1998. Four-year trends in Helicobacter pylori IgG serology following successful eradication. Am. J. Med. 105:18-20. - PubMed
-
- Evans, D. J., D. G. Evans, D. Y. Graham, and P. D. Klein. 1989. A sensitive and specific serologic test for detection of Campylobacter pylori infection. Gastroenterology 96:1004-1008. - PubMed
-
- Fallone, C. A., V. G. Loo, and A. N. Barkun. 1998. Utility of serology in determining Helicobacter pylori eradication after therapy. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 12:117-124. - PubMed
-
- Kato, M., Y. Yamaoka, J. J. Kim, R. Reddy, M. Asaka, K. Kashima, M. S. Osato, F. A. K. El-Zaatari, D. Y. Graham, and D. H. Kwon. 2000. Regional differences in metronidazole resistance and increasing clarithromycin resistance among Helicobacter pylori isolates from Japan. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 44:2214-2216. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kim, J. J., R. Reddy, M. Lee, J. G. Kim, F. A. K. El-Zaatari, M. S. Osato, D. Y. Graham, and D. H. Kwon. 2001. Analysis of metronidazole, clarithromycin and tetracycline resistance of Helicobacter pylori isolates from Korea. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 47:459-461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

