uPAR and HER-2 gene status in individual breast cancer cells from blood and tissues
- PMID: 17079488
- PMCID: PMC1838539
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0608113103
uPAR and HER-2 gene status in individual breast cancer cells from blood and tissues
Abstract
Overexpression of urokinase plasminogen activator system or HER-2 (erbB-2) in breast cancer is associated with a poor prognosis. HER-2 overexpression is caused by HER-2 gene amplification. The anti-HER-2 antibody trastuzumab significantly improves clinical outcome for HER2-positive breast cancer. Drugs that target the uPA system are in early clinical trials. The aims of this study were to determine whether urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) gene amplification occurs and whether analysis of individual tumor cells (TCs) in the blood or tissue can add information to conventional pathological analysis that could help in diagnosis and treatment. Analysis of individual TCs indicates that uPAR amplification occurs in a significant portion of primary breast cancers and also circulating tumor cells (CTCs) from patients with advanced disease. There was complete concordance between touch preps (TPs) and conventional pathological examination of HER-2 and uPAR gene status in primary tumors. There was also excellent concordance of HER-2 gene status between primary tumors and CTCs provided that acquisition of HER-2 gene amplification in CTCs was taken into account. Unexpectedly, gene amplification of HER-2 and uPAR occurred most frequently in the same TC and patient, suggesting a biological bias and potential advantage for coamplification. Expression of HER-2 and uPAR in primary tumors predicted gene status in 100 and 92% of patients, respectively.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: J.U. holds stock in Immunicon Corporation.
Figures

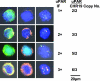
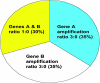
Comment in
-
Circulating tumor cells in breast cancer: Advanced tools for "tailored" therapy?Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Nov 14;103(46):17073-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608651103. Epub 2006 Nov 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17090687 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs H, Paton V, Bajamonde A, Fleming T, Eiermann W, Wolter J, Pegram M, et al. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:783–792. - PubMed
-
- Romond EH, Perez EA, Bryant J, Suman VJ, Geyer CE, Jr, Davidson NE, Tan-Chiu E, Martino S, Paik S, Kaufman PA, et al. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1673–1684. - PubMed
-
- Piccart-Gebhart MJ, Procter M, Leyland-Jones B, Goldhirsch A, Untch M, Smith I, Gianni L, Baselga J, Bell R, Jackisch C, et al. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1659–1672. - PubMed
-
- Yeon CH, Pegram MD. Invest New Drugs. 2005;23:391–409. - PubMed
-
- Ross JS, Fletcher JA, Bloom KJ, Linette GP, Stec J, Summans WF, Pusztai L, Hortobagyi GN. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2004;3:379–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

