The striatal-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase gates long-term potentiation and fear memory in the lateral amygdala
- PMID: 17081505
- PMCID: PMC1853327
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.08.005
The striatal-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase gates long-term potentiation and fear memory in the lateral amygdala
Abstract
Background: Formation of long-term memories is critically dependent on extracellular-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling. Activation of the ERK pathway by the sequential recruitment of mitogen-activated protein kinases is well understood. In contrast, the proteins that inactivate this pathway are not as well characterized.
Methods: Here we tested the hypothesis that the brain-specific striatal-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase (STEP) plays a key role in neuroplasticity and fear memory formation by its ability to regulate ERK1/2 activation.
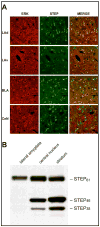
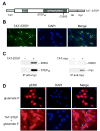
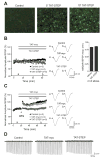
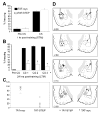
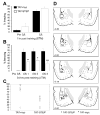
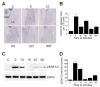
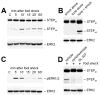
Results: STEP co-localizes with the ERKs within neurons of the lateral amygdala. A substrate-trapping STEP protein binds to the ERKs and prevents their nuclear translocation after glutamate stimulation in primary cell cultures. Administration of TAT-STEP into the lateral amygdala (LA) disrupts long-term potentiation (LTP) and selectively disrupts fear memory consolidation. Fear conditioning induces a biphasic activation of ERK1/2 in the LA with an initial activation within 5 minutes of training, a return to baseline levels by 15 minutes, and an increase again at 1 hour. In addition, fear conditioning results in the de novo translation of STEP. Inhibitors of ERK1/2 activation or of protein translation block the synthesis of STEP within the LA after fear conditioning.
Conclusions: Together, these data imply a role for STEP in experience-dependent plasticity and suggest that STEP modulates the activation of ERK1/2 during amygdala-dependent memory formation. The regulation of emotional memory by modulating STEP activity may represent a target for the treatment of psychiatric disorders such as posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), panic, and anxiety disorders.
Figures
References
-
- Aarts M, Liu Y, Liu L, Besshoh S, Arundine M, Gurd JW, Wang YT, Salter MW, Tymianski M. Treatment of ischemic brain damage by perturbing NMDA receptor- PSD-95 protein interactions. Science. 2002;29:846–850. - PubMed
-
- Atkins CM, Selcher JC, Petraitis JJ, Trzaskos JM, Sweatt JD. The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat Neurosci. 1998;1:602–609. - PubMed
-
- Blair HT, Schafe GE, Bauer EP, Rodrigues SM, LeDoux JE. Synaptic plasticity in the lateral amygdala: a cellular hypothesis of fear conditioning. Learn Mem. 2001;8:229–242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

