Rolipram: a specific phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor with potential antipsychotic activity
- PMID: 17081698
- PMCID: PMC3313447
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.09.026
Rolipram: a specific phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor with potential antipsychotic activity
Abstract
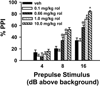
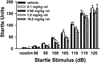
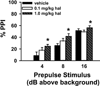
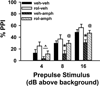
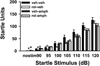
Currently available antipsychotic medications work primarily by antagonizing D2 dopamine receptors, thus raising intracellular cAMP levels. We hypothesized that intracellular stimulation of cAMP levels in the CNS would have similar effects to treatment with antipsychotic medication. To test this hypothesis, we studied the effect of an acute treatment of rolipram, an inhibitor of type 4 phosphodiesterases that degrade cAMP, on acoustic startle and prepulse inhibition (PPI) of the acoustic startle response in C57BL/6J mice known to exhibit poor PPI. PPI is disrupted in schizophrenia patients, and the ability of a drug to increase PPI in mice is predictive of antipsychotic efficacy. We show here that acute treatment with rolipram significantly increases PPI at doses that do not alter the acoustic startle response (lowest effective dose 0.66 mg/kg). In addition, rolipram (0.66 mg/kg) blocks the disruptive effects of amphetamine (10 mg/kg) on PPI. At a slightly higher dose (1.0 mg/kg), rolipram also induces catalepsy. Thus, phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibition has many of the same behavioral effects as traditional antipsychotic medications. In contrast to traditional antipsychotics, these effects are achieved through alteration of an intracellular second messenger system rather than antagonism of neurotransmitter receptors. Given previous reports showing rolipram improves cognition, we conclude that PDE4 represents an important novel target for further antipsychotic drug development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antipsychotic-like properties of phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors: evaluation of 4-(3-butoxy-4-methoxybenzyl)-2-imidazolidinone (RO-20-1724) with auditory event-related potentials and prepulse inhibition of startle.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008 Jul;326(1):230-9. doi: 10.1124/jpet.108.138586. Epub 2008 Apr 17. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008. PMID: 18420599
-
Antipsychotic profile of rolipram: efficacy in rats and reduced sensitivity in mice deficient in the phosphodiesterase-4B (PDE4B) enzyme.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2007 Jun;192(3):415-24. doi: 10.1007/s00213-007-0727-x. Epub 2007 Mar 2. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2007. PMID: 17333137
-
Suppression of oro-facial movements by rolipram, a cAMP phosphodiesterase inhibitor, in rats chronically treated with haloperidol.Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Aug 25;282(1-3):71-6. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(95)00278-s. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 7498291
-
The antidepressant and antiinflammatory effects of rolipram in the central nervous system.CNS Drug Rev. 2001 Winter;7(4):387-98. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3458.2001.tb00206.x. CNS Drug Rev. 2001. PMID: 11830756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disrupted in schizophrenia 1: building brains and memories.Trends Mol Med. 2006 Jun;12(6):255-61. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2006.04.009. Epub 2006 May 6. Trends Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 16679065 Review.
Cited by
-
Further Insights in the Binding Mode of Selective Inhibitors to Human PDE4D Enzyme Combining Docking and Molecular Dynamics.Mol Inform. 2016 Sep;35(8-9):369-81. doi: 10.1002/minf.201501033. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Mol Inform. 2016. PMID: 27546041 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral and neurochemical characterization of mice deficient in the phosphodiesterase-4B (PDE4B) enzyme.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008 Mar;197(1):115-26. doi: 10.1007/s00213-007-1014-6. Epub 2007 Dec 1. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008. PMID: 18060387
-
Critical role of nitric oxide in the modulation of prepulse inhibition in Swiss mice.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Feb;231(4):663-72. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3277-4. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24101156
-
Efficient Synthesis of β-Aryl-γ-lactams and Their Resolution with (S)-Naproxen: Preparation of (R)- and (S)-Baclofen.Molecules. 2015 Dec 10;20(12):22028-43. doi: 10.3390/molecules201219830. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26690390 Free PMC article.
-
Sensorimotor gating in neurotensin-1 receptor null mice.Neuropharmacology. 2010 Jan;58(1):173-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.07.002. Epub 2009 Jul 9. Neuropharmacology. 2010. PMID: 19596359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adell A, Artigas F. The somatodendritic release of dopamine in the ventral tegmental area and its regulation by afferent transmitter systems. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2004;28:415–431. - PubMed
-
- Beavo JA, Brunton LL. Cyclic nucleotide research: still expanding after half a century. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:710–718. - PubMed
-
- Bonbon D, Breulet M, Gerard-Vandenhove M, Guiot-Goffioul F, Plomteux G, Sastre-y-Hernandez M, Schratzer M, Troisfontaines B, van Frenckeill R, Wachtel H. Is phosphodiesterase inhibition a new mechanism of antidepressant action? A double blind double-dummy study between rolipram and desipramine in hospitalized major and/or endogenous depressives. Eur Arch Psychiatry Neurol Sci. 1988;238:2–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

