From the Academy: Colloquium review. Unique characteristics of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae AvrXa21 and implications for plant innate immunity
- PMID: 17082309
- PMCID: PMC1693675
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0605508103
From the Academy: Colloquium review. Unique characteristics of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae AvrXa21 and implications for plant innate immunity
Abstract
This article provides a brief overview of some of the major concepts and molecular features of plant and animal innate immune systems. The rice pathogen recognition receptor, XA21, confers resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae strains producing the AvrXa21 elicitor. Xa21 codes for a receptor-like kinase consisting of an extracellular leucine-rich repeat domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic kinase domain. We show that AvrXa21 activity requires the presence of rax (required for AvrXa21) A, raxB, and raxC genes that encode components of a type one secretion system. In contrast, an hrpC(-) strain deficient in type three secretion maintains AvrXa21 activity. Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris can express AvrXa21 activity if raxST, encoding a putative sulfotransferase, and raxA are provided in trans. Expression of rax genes depends on population density and other functioning rax genes. This and other data suggest that the AvrXa21 pathogen-associated molecule is involved in quorum sensing. Together these data suggest that AvrXa21 represents a previously uncharacterized class of Gram-negative bacterial signaling molecules. These results from our studies of the XA21/AvrXa21 interaction call for some modifications in the way we think about innate immunity strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

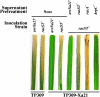
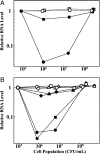
Similar articles
-
Bacterial genes involved in type I secretion and sulfation are required to elicit the rice Xa21-mediated innate immune response.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2004 Jun;17(6):593-601. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2004.17.6.593. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2004. PMID: 15195942
-
RaxH/RaxR: a two-component regulatory system in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae required for AvrXa21 activity.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2004 Jun;17(6):602-12. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2004.17.6.602. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2004. PMID: 15195943
-
The Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae PhoPQ two-component system is required for AvrXA21 activity, hrpG expression, and virulence.J Bacteriol. 2008 Mar;190(6):2183-97. doi: 10.1128/JB.01406-07. Epub 2008 Jan 18. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18203830 Free PMC article.
-
[Advances of rice bacterial blight disease resistance gene Xa21].Yi Chuan. 2006 Jun;28(6):745-53. Yi Chuan. 2006. PMID: 16818441 Review. Chinese.
-
The Role of RaxST, a Prokaryotic Sulfotransferase, and RaxABC, a Putative Type I Secretion System, in Activation of the Rice XA21-Mediated Immune Response.Scientifica (Cairo). 2014;2014:532816. doi: 10.1155/2014/532816. Epub 2014 Oct 19. Scientifica (Cairo). 2014. PMID: 25386383 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RaxM regulates the AvrXa21 (RaxX)-mediated immune response.Mol Plant Pathol. 2018 Nov;19(11):2363-2369. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12703. Epub 2018 Sep 4. Mol Plant Pathol. 2018. PMID: 30011129 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP3 regulates XA21-mediated innate immunity in rice.PLoS One. 2010 Feb 17;5(2):e9262. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009262. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20174657 Free PMC article.
-
Resistant and susceptible responses in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) to bacterial stem blight caused by Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae.PLoS One. 2017 Dec 15;12(12):e0189781. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189781. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29244864 Free PMC article.
-
Unifying themes in microbial associations with animal and plant hosts described using the gene ontology.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2010 Dec;74(4):479-503. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00017-10. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2010. PMID: 21119014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An ATPase promotes autophosphorylation of the pattern recognition receptor XA21 and inhibits XA21-mediated immunity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Apr 27;107(17):8029-34. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0912311107. Epub 2010 Apr 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20385831 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Girardin SE, Sansonetti PJ, Philpott DJ. Trends Microbiol. 2002;10:193–199. - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov R, Janeway CA., Jr Cell. 1997;91:295–298. - PubMed
-
- Janeway CA, Jr, Medzhitov R. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:197–216. - PubMed
-
- Ramos HC, Rumbo M, Sirard JC. Trends Microbiol. 2004;12:509–517. - PubMed
-
- Leulier F, Parquet C, Pili-Floury S, Ryu JH, Caroff M, Lee WJ, Mengin-Lecreulx D, Lemaitre B. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:478–484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

