Cutting edge: inherent and acquired resistance to radiation-induced apoptosis in B cells: a pivotal role for STAT3
- PMID: 17082570
- PMCID: PMC2770730
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.10.6593
Cutting edge: inherent and acquired resistance to radiation-induced apoptosis in B cells: a pivotal role for STAT3
Abstract
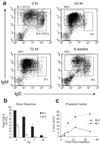
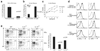
Radiation-induced apoptosis (RiA) is used therapeutically for tumor cell ablation as well as a tool to characterize hemopoietic cell lineages. We report that the peritoneal B-1 B cell subset is selectively resistant to RiA. Inherent radioresistance is not shared by splenic B-2 or B-1 cells. However, it is conferred upon B-2 cells by BCR crosslinking in the presence of IL-6 or IL-10. In vivo experiments with gene-targeted mice confirm that IL-6 and, to a lesser extent, IL-10 are the relevant stimuli that combine with BCR ligands to promote B-1 cell radioresistance. STAT3 promotes cell survival in response to selected growth factors, and is activated by combined BCR crosslinking and IL-6 (IL-10). Importantly, STAT3(-/-) B-1 cells become susceptible to irradiation, indicating that STAT3 activation by the BCR in the presence of IL costimuli account for the inherent radioresistance of peritoneal B-1 B cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Berland R, Wortis HH. Origins and functions of B-1 cells with notes on the role of CD5. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002;20:253–300. - PubMed
-
- Montecino-Rodriguez E, Leathers H, Dorshkind K. Identification of a B-1 B cell-specified progenitor. Nat. Immunol. 2006;7:293–301. - PubMed
-
- Hayakawa K, Asano M, Shinton SA, Gui M, Allman D, Stewart CL, Silver J, Hardy RR. Positive selection of natural autoreactive B cells. Science. 1999;285:113–116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

