Airway epithelial cells produce B cell-activating factor of TNF family by an IFN-beta-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 17082634
- PMCID: PMC2804942
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.10.7164
Airway epithelial cells produce B cell-activating factor of TNF family by an IFN-beta-dependent mechanism
Abstract
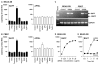
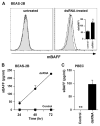
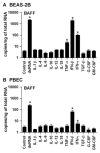
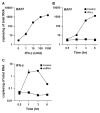
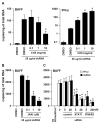
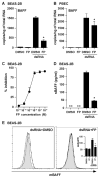
Activation of B cells in the airways is now believed to be of great importance in immunity to pathogens, and it participates in the pathogenesis of airway diseases. However, little is known about the mechanisms of local activation of B cells in airway mucosa. We investigated the expression of members of the B cell-activating TNF superfamily (B cell-activating factor of TNF family (BAFF) and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL)) in resting and TLR ligand-treated BEAS-2B cells and primary human bronchial epithelial cells (PBEC). In unstimulated cells, expression of BAFF and APRIL was minimal. However, BAFF mRNA was significantly up-regulated by TLR3 ligand (dsRNA), but not by other TLR ligands, in both BEAS-2B cells (376-fold) and PBEC (224-fold). APRIL mRNA was up-regulated by dsRNA in PBEC (7-fold), but not in BEAS-2B cells. Membrane-bound BAFF protein was detectable after stimulation with dsRNA. Soluble BAFF protein was also induced by dsRNA (> 200 pg/ml). The biological activity of the epithelial cell-produced BAFF was verified using a B cell survival assay. BAFF was also strongly induced by IFN-beta, a cytokine induced by dsRNA. Induction of BAFF by dsRNA was dependent upon protein synthesis and IFN-alphabeta receptor-JAK-STAT signaling, as indicated by studies with cycloheximide, the JAK inhibitor I, and small interfering RNA against STAT1 and IFN-alphabeta receptor 2. These results suggest that BAFF is induced by dsRNA in airway epithelial cells and that the response results via an autocrine pathway involving IFN-beta. The production of BAFF and APRIL by epithelial cells may contribute to local accumulation, activation, class switch recombination, and Ig synthesis by B cells in the airways.
Figures
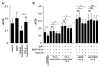
Similar articles
-
The BAFF/APRIL system: emerging functions beyond B cell biology and autoimmunity.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013 Jun;24(3):203-15. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.04.003. Epub 2013 May 15. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013. PMID: 23684423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cooperative activation of CCL5 expression by TLR3 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha or interferon-gamma through nuclear factor-kappaB or STAT-1 in airway epithelial cells.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2010;152 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):9-17. doi: 10.1159/000312120. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20523058 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of epithelial signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 activation by extracts of Aspergillus fumigatus.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015 Jul;53(1):87-95. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2014-0333OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25474274 Free PMC article.
-
A BAFF/APRIL-dependent TLR3-stimulated pathway enhances the capacity of rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts to induce AID expression and Ig class-switching in B cells.Ann Rheum Dis. 2011 Oct;70(10):1857-65. doi: 10.1136/ard.2011.150219. Epub 2011 Jul 27. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011. PMID: 21798884
-
The roles of B cell activation factor (BAFF) and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL) in allergic asthma.Immunol Lett. 2020 Sep;225:25-30. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2020.06.001. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Immunol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32522667 Review.
Cited by
-
The BAFF/APRIL system: emerging functions beyond B cell biology and autoimmunity.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013 Jun;24(3):203-15. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.04.003. Epub 2013 May 15. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013. PMID: 23684423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription of interleukin-25 and extracellular release of the protein is regulated by allergen proteases in airway epithelial cells.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 Nov;49(5):741-50. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0304OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23590308 Free PMC article.
-
Considerations for Novel COVID-19 Mucosal Vaccine Development.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Jul 23;10(8):1173. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10081173. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35893822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross-talk between human mast cells and bronchial epithelial cells in plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 production via transforming growth factor-β1.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015 Jan;52(1):88-95. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0399OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 24987792 Free PMC article.
-
The BAFF-APRIL System in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 16;15(6):1791. doi: 10.3390/cancers15061791. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980677 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hogg JC, Eggleston PA. Is asthma an epithelial disease? Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984;129:207–208. - PubMed
-
- Cohn LA, Adler KB. Interactions between airway epithelium and mediators of inflammation. Exp Lung Res. 1992;18:299–322. - PubMed
-
- Rennard SI, Romberger DJ, Sisson JH, Von Essen SG, Rubinstein I, Robbins RA, Spurzem JR. Airway epithelial cells: functional roles in airway disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994;150:S27–S30. - PubMed
-
- Abreu MT, Fukata M, Arditi M. TLR signaling in the gut in health and disease. J Immunol. 2005;174:4453–4460. - PubMed
-
- Diamond G, Legarda D, Ryan LK. The innate immune response of the respiratory epithelium. Immunol Rev. 2000;173:27–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

