Reducing HIV transmission risk by increasing serostatus disclosure: a mathematical modeling analysis
- PMID: 17082982
- PMCID: PMC2408867
- DOI: 10.1007/s10461-006-9187-2
Reducing HIV transmission risk by increasing serostatus disclosure: a mathematical modeling analysis
Abstract
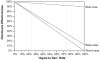
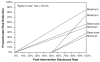
Persons living with HIV infection are encouraged to disclose their HIV-positive serostatus to prospective sex partners to decrease the likelihood of unsafe sex and HIV transmission. However, the effectiveness of serostatus disclosure as a preventive measure is not known. We developed a mathematical framework for assessing the HIV transmission risk reduction effectiveness of serostatus disclosure, examined how increasing the disclosure rate affects the transmission risk reduction effectiveness of disclosure, and explored the interaction between condom use and disclosure effectiveness. Under base-case assumptions, serostatus disclosure reduced the risk of HIV transmission by between 17.9% and 40.6% relative to no disclosure. Increasing the disclosure rate from the base-case value of 51.9-75.7% produced a 26.2-59.2% reduction in risk. The findings of this modeling study strongly support intervention efforts to increase both serostatus disclosure and condom use by persons living with HIV.
Figures

References
-
- Center for Disease Control . HIV Prevention Strategic Plan through 2005. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Atlanta: 2001.
-
- Crepaz N, Lyles CM, Wolitski RJ, Passin WF, Rama SM, Herbst JH, et al. Do prevention interventions reduce HIV risk behaviours among people living with HIV? A meta-analytic review of controlled trials. AIDS. 2006;20:143–157. - PubMed
-
- De Rosa CJ, Marks G. Preventive counseling of HIV-positive men and self-disclosure of serostatus to sex partners: New opportunities for prevention. Health Psychology. 1998;17:224–231. - PubMed
-
- Kalichman SC, Nachimson D. Self-efficacy and disclosure of HIV-positive serostatus to sex partners. Health Psychology. 1999;18:281–287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

