The common gamma chain cytokines interleukin (IL)-2 and IL-7 indirectly modulate blood fluke development via effects on CD4+ T cells
- PMID: 17083048
- PMCID: PMC2853799
- DOI: 10.1086/508896
The common gamma chain cytokines interleukin (IL)-2 and IL-7 indirectly modulate blood fluke development via effects on CD4+ T cells
Abstract
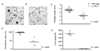
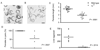
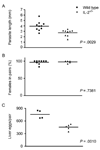
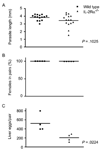
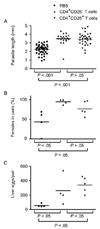
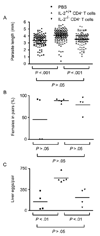
The human pathogen Schistosoma mansoni exhibits a highly evolved and intricate relationship with its host, evading immune destruction while co-opting CD4(+) T cell-driven mechanisms to facilitate parasite development and egg excretion. Because the common gamma ( gamma (c)) chain cytokine interleukin (IL)-7 is also implicated in modulating schistosome development, we investigated whether this effect is mediated indirectly through the essential role that IL-7 plays in CD4(+) T cell growth and survival. We demonstrate that attenuated schistosome development in the absence of IL-7 results from dysregulated T cell homeostasis and not from disruption of direct interactions between schistosomes and IL-7. We also identify an indirect role that another gamma (c) chain cytokine plays in schistosome development, demonstrating that IL-2 expression by CD4(+) T cells is essential for normal parasite development. Thus, cytokines critical for CD4(+) T cell survival and function can mediate indirect but potent effects on developing schistosomes and underscore the importance of CD4(+) T cells in facilitating schistosome development.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest: none reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Naturally occurring CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells are an essential, IL-10-independent part of the immunoregulatory network in Schistosoma mansoni egg-induced inflammation.J Immunol. 2006 May 1;176(9):5374-87. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.9.5374. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16622005
-
Modulation of blood fluke development in the liver by hepatic CD4+ lymphocytes.Science. 2001 Nov 9;294(5545):1358-61. doi: 10.1126/science.1064462. Science. 2001. PMID: 11701932
-
T-bet protects against exacerbation of schistosome egg-induced immunopathology by regulating Th17-mediated inflammation.Eur J Immunol. 2009 Sep;39(9):2470-81. doi: 10.1002/eji.200939325. Eur J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19714576 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an antipathology vaccine for schistosomiasis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1996 Oct 25;797:191-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1996.tb52960.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1996. PMID: 8993362 Review.
-
Priming of the immune response by schistosome eggs.Parasite Immunol. 2005 Jul-Aug;27(7-8):265-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.2005.00765.x. Parasite Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16138847 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of adult worms and granulomatous pathology are collectively regulated by T- and B-cells in mice infected with Schistosoma japonicum.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54432. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054432. Epub 2013 Jan 22. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23349889 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of T cell deficiency on the development of worms and granuloma formation in mice infected with Schistosoma japonicum.Parasitol Res. 2008 May;102(6):1129-34. doi: 10.1007/s00436-008-0880-0. Epub 2008 Feb 2. Parasitol Res. 2008. PMID: 18246371
-
Interleukin (IL)-33 is dispensable for Schistosoma mansoni worm maturation and the maintenance of egg-induced pathology in intestines of infected mice.Parasit Vectors. 2021 Jan 22;14(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04561-w. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 33482904 Free PMC article.
-
Conservation of CD4+ T cell-dependent developmental mechanisms in the blood fluke pathogens of humans.Int J Parasitol. 2007 Mar;37(3-4):405-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2006.11.001. Epub 2006 Dec 13. Int J Parasitol. 2007. PMID: 17196594 Free PMC article.
-
Gene discovery for the carcinogenic human liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini.BMC Genomics. 2007 Jun 22;8:189. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-189. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17587442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Georgi JR, Wade SE, Dean DA. Attrition and temporal distribution of Schistosoma mansoni and S. haematobium schistosomula in laboratory mice. Parasitology. 1986;93:55–70. - PubMed
-
- Georgi JR, Wade SE, Dean DA. Schistosoma mansoni: mechanism of attrition and routes of migration from lungs to hepatic portal system in the laboratory mouse. J Parasitol. 1987;73:706–711. - PubMed
-
- Pearce EJ, MacDonald AS. The immunobiology of schistosomiasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:499–511. - PubMed
-
- Davies SJ, Grogan JL, Blank RB, Lim KC, Locksley RM, McKerrow JH. Modulation of blood fluke development in the liver by hepatic CD4+ lymphocytes. Science. 2001;294:1358–1361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

