Molecular mechanisms of resistance and toxicity associated with platinating agents
- PMID: 17084534
- PMCID: PMC1855222
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2006.09.006
Molecular mechanisms of resistance and toxicity associated with platinating agents
Abstract
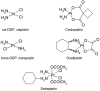
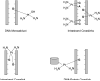
Platinating agents, including cisplatin, carboplatin, and oxaliplatin, have been used clinically for nearly 30years as part of the treatment of many types of cancers, including head and neck, testicular, ovarian, cervical, lung, colorectal and relapsed lymphoma. The cytotoxic lesion of platinating agents is thought to be the platinum intrastrand crosslink that forms on DNA, although treatment activates a number of signal transduction pathways. Treatment with these agents is characterized by resistance, both acquired and intrinsic. This resistance can be caused by a number of cellular adaptations, including reduced uptake, inactivation by glutathione and other anti-oxidants, and increased levels of DNA repair or DNA tolerance. Here we investigate the pathways that treatment with platinating agents activate, the mechanisms of resistance, potential candidate genes involved in the development of resistance, and associated clinical toxicities. Although the purpose of this review is to provide an overview of cisplatin, carboplatin, and oxaliplatin, we have focused primarily on preclinical data that has clinical relevance generated over the past five years.
Figures


References
-
- Rosenberg B, et al. Platinum compounds: a new class of potent antitumour agents. Nature. 1969;222(191):385–6. - PubMed
-
- Kartalou M, Essigmann JM. Mechanisms of resistance to cisplatin. Mutat Res. 2001;478(12):23–43. - PubMed
-
- Wang D, Lippard SJ. Cellular processing of platinum anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4(4):307–20. - PubMed
-
- Samimi G, et al. Novel mechanisms of platinum drug resistance identified in cells selected for resistance to JM118 the active metabolite of satraplatin. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2006 - PubMed
-
- Sternberg CN, et al. Phase III trial of satraplatin, an oral platinum plus prednisone vs. prednisone alone in patients with hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Oncology. 2005;68(1):2–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

