Chemotherapy-evoked painful peripheral neuropathy: analgesic effects of gabapentin and effects on expression of the alpha-2-delta type-1 calcium channel subunit
- PMID: 17084535
- PMCID: PMC1805704
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.09.044
Chemotherapy-evoked painful peripheral neuropathy: analgesic effects of gabapentin and effects on expression of the alpha-2-delta type-1 calcium channel subunit
Abstract
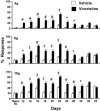
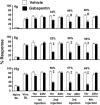
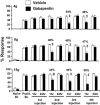
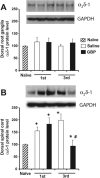
Chemotherapeutics in the taxane and vinca-alkaloid classes sometimes produce a painful peripheral neuropathy for which there is no validated treatment. Experiments with rat models of paclitaxel- and vincristine-evoked pain suggest that these conditions may not respond to all of the analgesics that have efficacy in other models of painful peripheral neuropathy. We tested gabapentin as a potential analgesic for paclitaxel- and vincristine-evoked pain. We used a repeated dosing paradigm because there are precedents showing that repeated drug exposure may be necessary to demonstrate analgesia in neuropathic pain models. Gabapentin is believed to work via binding to voltage-gated calcium channels that contain the alpha-2-delta type-1 (alpha(2)delta-1) subunit, and the expression of this subunit is known to be increased in some painful peripheral neuropathy models. Thus we also examined whether the paclitaxel-evoked pain syndrome was accompanied by an alpha(2)delta-1 increase, and whether gabapentin had any effect on subunit expression. We found that the paclitaxel- and vincristine-evoked mechano-allodynia and mechano-hyperalgesia were significantly reduced by gabapentin, but only with repeated dosing. Paclitaxel-evoked painful peripheral neuropathy was associated with an increased expression of the alpha(2)delta-1 subunit in the spinal dorsal horn, but not in the dorsal root ganglia. The spinal cord increase was normalized by repeated gabapentin injections. Together, these findings suggest that repeated dosing with gabapentin may be beneficial in patients with chemotherapy-evoked painful peripheral neuropathy and that gabapentin's mechanisms of action may include normalization of the nerve injury-evoked increase in calcium channel alpha(2)delta-1 subunit expression.
Figures
References
-
- Bian F, Li Z, Offord JD, Davis MD, McCormick JA, Taylor CP, Walker LC. Calcium channel alpha2-delta type I subunit is the major binding protein for pregabalin in neocortex, hippocampus, amygdale, and spinal cord: an ex vivo autoradiographic study in alpha2-delta type 1 genetically modified mice. Brain Res. 2006;1075:68–80. - PubMed
-
- Bosnjak S, Jelic S, Susnjar S, Luki V. Gabapentin for relief of neuropathic pain related to anticancer treatment: a preliminary study. J Chemother. 2002;14:214–219. - PubMed
-
- Caraceni A, Zecca E, Bonezzi C, Arcuri E, Yaya Tur R, Maltoni M, Visentin M, Gorni G, Martini C, Tirelli W, Barbieri M, De Conno F. Gabapentin for neuropathic cancer pain: randomized controlled trial from the Gabapentin Cancer Pain Study Group. Cancer Treat Rev. 2004;31:58–62.
-
- Costigan M, Befort K, Karchewski L, Griffin RS, D'Urso D, Allchorne A, Sitarski J, Mannion JW, Pratt RE, Woolf CJ. Replicate high-density rat genome oligonucleotide microarrays reveal hundreds of regulated genes in the dorsal root ganglion after peripheral nerve injury. BMC Neurosci. 2002;3:16. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dougherty PM, Cata JP, Cordella JV, Burton A, Weng HR. Taxol-induced sensory disturbance is characterized by preferential impairment of myelinated fiber function in cancer patients. Pain. 2004;109:132–142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

