Physiological roles of the light, oxygen, or voltage domains of phototropin 1 and phototropin 2 in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 17085510
- PMCID: PMC1761953
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.106.089839
Physiological roles of the light, oxygen, or voltage domains of phototropin 1 and phototropin 2 in Arabidopsis
Abstract
Phototropins (phot1 and phot2) are plant blue-light receptors that mediate phototropism, chloroplast movement, stomatal opening, rapid inhibition of growth of etiolated seedlings, and leaf expansion in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana). Their N-terminal region contains two light, oxygen, or voltage (LOV) domains, which bind flavin mononucleotide and form a covalent adduct between a conserved cysteine and the flavin mononucleotide chromophore upon photoexcitation. The C-terminal region contains a serine/threonine kinase domain that catalyzes blue-light-activated autophosphorylation. Here, we have transformed the phot1 phot2 (phot1-5 phot2-1) double mutant with PHOT expression constructs driven by the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. These constructs encode either wild-type phototropin or phototropin with one or both LOV-domain cysteines mutated to block their photochemistry. We selected multiple lines in each of the eight resulting categories of transformants for further physiological analyses. Specifically, we investigated whether LOV1 and LOV2 serve the same or different functions for phototropism and leaf expansion. Our results show that the LOV2 domain of phot1 plays a major role in phototropism and leaf expansion, as does the LOV2 domain of phot2. No complementation of phototropism or leaf expansion was observed for the LOV1 domain of phot1. However, phot2 LOV1 was unexpectedly found to complement phototropism to a considerable level. Similarly, transformants carrying a PHOT transgene with both LOV domains inactivated developed strong curvatures toward high fluence rate blue light. However, we found that the phot2-1 mutant is leaky and produces a small level of full-length phot2 protein. In vitro experiments indicate that cross phosphorylation can occur between functional phot2 and inactivated phot1 molecules. Such a mechanism may occur in vivo and therefore account for the functional activities observed in the PHOT transgenics with both lov domains inactivated. The implications of this mechanism with respect to phototropin function are discussed.
Figures

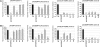

 +
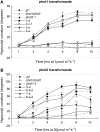
+  (series 4) transgenic lines (C) and the phot2
(series 4) transgenic lines (C) and the phot2 +
+  (series 8) transgenic lines (D) are shown. Responses of wild-type (gl1), phot1 phot2 double mutant, phot1-5 single, and phot2-1 single mutant are also shown.
(series 8) transgenic lines (D) are shown. Responses of wild-type (gl1), phot1 phot2 double mutant, phot1-5 single, and phot2-1 single mutant are also shown.

 ); lanes 3 and 4: phot1 kinase domain mutated (phot1
); lanes 3 and 4: phot1 kinase domain mutated (phot1 ); lanes 5 and 6: wild-type phot1; lanes 7 and 8: phot2 kinase domain mutated (phot2
); lanes 5 and 6: wild-type phot1; lanes 7 and 8: phot2 kinase domain mutated (phot2 ); lanes 9 and 10: wild-type phot2. D, Dark; L, light (saturating white light);
); lanes 9 and 10: wild-type phot2. D, Dark; L, light (saturating white light);  , LOV-domain mutated;
, LOV-domain mutated;  , kinase-domain mutated. Western-blot analysis of phot1 and phot2 protein levels is shown below. Soluble protein extracts prepared from insect cells were probed with anti-phot1 antibody (left) or anti-phot2 antibody (right).
, kinase-domain mutated. Western-blot analysis of phot1 and phot2 protein levels is shown below. Soluble protein extracts prepared from insect cells were probed with anti-phot1 antibody (left) or anti-phot2 antibody (right).
 ); lanes 3 and 4: phot2 with its kinase domain inactivated (phot2
); lanes 3 and 4: phot2 with its kinase domain inactivated (phot2 ) plus phot1 with its kinase domain inactivated (phot1
) plus phot1 with its kinase domain inactivated (phot1 ); lanes 5 and 6: functional phot2 plus phot1 with both LOV domains mutated (phot1
); lanes 5 and 6: functional phot2 plus phot1 with both LOV domains mutated (phot1 = phot1
= phot1 ); lanes 7 and 8: phot2 with its kinase domain inactivated (phot2
); lanes 7 and 8: phot2 with its kinase domain inactivated (phot2 ) plus phot1 both LOV domains mutated (phot1
) plus phot1 both LOV domains mutated (phot1 = phot2
= phot2 ). Inactivation of the proteins is as described in Figure 6. Western-blot analysis of phot1 and phot2 protein levels is shown below. Soluble protein extracts prepared from insect cells were probed with anti-phot1 antibody (left) or anti-phot2 antibody (right).
). Inactivation of the proteins is as described in Figure 6. Western-blot analysis of phot1 and phot2 protein levels is shown below. Soluble protein extracts prepared from insect cells were probed with anti-phot1 antibody (left) or anti-phot2 antibody (right).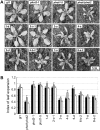
Similar articles
-
Phototropin LOV domains exhibit distinct roles in regulating photoreceptor function.Plant J. 2002 Oct;32(2):205-19. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01415.x. Plant J. 2002. PMID: 12383086
-
Photochemical properties of the flavin mononucleotide-binding domains of the phototropins from Arabidopsis, rice, and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Plant Physiol. 2002 Jun;129(2):762-73. doi: 10.1104/pp.002410. Plant Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12068117 Free PMC article.
-
Photosensitivity of kinase activation by blue light involves the lifetime of a cysteinyl-flavin adduct intermediate, S390, in the photoreaction cycle of the LOV2 domain in phototropin, a plant blue light receptor.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 30;287(49):40972-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.406512. Epub 2012 Oct 12. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23066024 Free PMC article.
-
Phototropin blue-light receptors.Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2007;58:21-45. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.58.032806.103951. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2007. PMID: 17067285 Review.
-
The phototropin family as photoreceptors for blue light-induced chloroplast relocation.J Plant Res. 2003 Feb;116(1):77-82. doi: 10.1007/s10265-002-0072-4. Epub 2002 Dec 21. J Plant Res. 2003. PMID: 12605303 Review.
Cited by
-
A chemical genetic approach to engineer phototropin kinases for substrate labeling.J Biol Chem. 2018 Apr 13;293(15):5613-5623. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.001834. Epub 2018 Feb 23. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29475950 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of Arabidopsis phototropin 1 in the hypocotyl apex.Plant J. 2016 Dec;88(6):907-920. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13313. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Plant J. 2016. PMID: 27545835 Free PMC article.
-
Domain Organization in Plant Blue-Light Receptor Phototropin2 of Arabidopsis thaliana Studied by Small-Angle X-ray Scattering.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 10;21(18):6638. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186638. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32927860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytochrome Kinase Substrate 4 is phosphorylated by the phototropin 1 photoreceptor.EMBO J. 2012 Aug 15;31(16):3457-67. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.186. Epub 2012 Jul 10. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22781128 Free PMC article.
-
A blue light inducible two-component signal transduction system in the plant pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato.Biophys J. 2008 Feb 1;94(3):897-905. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.108977. Epub 2007 Sep 28. Biophys J. 2008. PMID: 17905842 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Batschauer A (2005) Plant cryptochromes: their genes, biochemistry, and physiological roles. In WR Briggs, JL Spudich, eds, Handbook of Photosensory Receptors. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany, pp 211–246
-
- Briggs WR, Christie JM (2002) Phototropins 1 and 2: versatile plant blue-light receptors. Trends Plant Sci 7 204–210 - PubMed
-
- Celaya RB, Liscum E (2005) Phototropins and associated signaling: providing the power of movement in higher plants. Photochem Photobiol 81 73–80 - PubMed
-
- Christie JM, Briggs WR (2005) Blue light sensing and signaling by the phototropins. In WR Briggs, JL Spudich, eds, Handbook of Photosensory Receptors. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany, pp 277–303
-
- Christie JM, Reymond P, Powell G, Bernasconi P, Reibekas AA, Liscum E, Briggs WR (1998) Arabidopsis NPH1: a flavoprotein with the properties of a photoreceptor for phototropism. Science 282 1698–1701 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

