Ubc9 interacts with Lu/BCAM adhesion glycoproteins and regulates their stability at the membrane of polarized MDCK cells
- PMID: 17087659
- PMCID: PMC1798433
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20060861
Ubc9 interacts with Lu/BCAM adhesion glycoproteins and regulates their stability at the membrane of polarized MDCK cells
Abstract
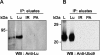
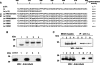
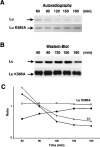
Lu (Lutheran) blood group and BCAM (basal cell adhesion molecule) antigens both reside on two gp (glycoprotein) isoforms, Lu and Lu(v13), that differ by the size of their cytoplasmic tail. They are receptors of laminin-10/11 and are expressed in RBCs (red blood cells), epithelial cells of multiple tissues and vascular endothelial cells. To gain more insights into the biological function of Lu/BCAM gps, we looked for potential partners of their cytoplasmic tail. We isolated Ubc9 (ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme 9) protein by screening a human kidney library using the yeast two-hybrid system. Lu/Ubc9 interaction was validated by GST (glutathione S-transferase) pull-down and co-immunoprecipitation experiments. Endogenous Ubc9 formed a complex with endogenous or recombinant Lu gp in A498 and MDCK (Madin-Darby canine kidney) epithelial cells respectively. Replacement of Lys(585) by alanine in the Lu gp abolished in vitro and ex vivo interactions of Lu gp with Ubc9 protein. Lu K585A mutant transfected in MDCK cells exhibited a normal basolateral membrane expression but was overexpressed at the surface of polarized MDCK cells as compared with wild-type Lu. Pulse-chase experiments showed extended half-life of Lu K585A gp at the plasma membrane, suggesting an impaired endocytosis of this mutant leading to protein accumulation at the membrane. Furthermore, we showed that the ability of MDCK-Lu K585A cells to spread on immobilized laminin was dramatically decreased. Our results support a physiological role for the direct interaction between Lu gp and Ubc9 protein and reveal a role for this enzyme in regulating the stability of Lu gp at the cell membrane.
Figures


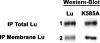

References
-
- Cartron J. P., Colin Y. Structural and functional diversity of blood group antigens. Transfus. Clin. Biol. 2001;8:163–199. - PubMed
-
- Daniels G. Terminology for red cell antigens – 1999 update. Immunohematology. 1999;15:95–99. - PubMed
-
- El Nemer W., Rahuel C., Colin Y., Gane P., Cartron J. P., Le Van Kim C. Organization of the human LU gene and molecular basis of the Lu(a)/Lu(b) blood group polymorphism. Blood. 1997;89:4608–4616. - PubMed
-
- Rahuel C., Le Van Kim C., Mattei M. G., Cartron J. P., Colin Y. A unique gene encodes spliceoforms of the B-cell adhesion molecule cell surface glycoprotein of epithelial cancer and of the Lutheran blood group glycoprotein. Blood. 1996;88:1865–1872. - PubMed
-
- El Nemer W., Gane P., Colin Y., Bony V., Rahuel C., Galacteros F., Cartron J. P., Le Van Kim C. The Lutheran blood group glycoproteins, the erythroid receptors for laminin, are adhesion molecules. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:16686–16693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

