Association between reduced heart rate variability and cognitive impairment in older disabled women in the community: Women's Health and Aging Study I
- PMID: 17087704
- PMCID: PMC2276586
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2006.00940.x
Association between reduced heart rate variability and cognitive impairment in older disabled women in the community: Women's Health and Aging Study I
Abstract
Objectives: To examine the independent association between heart rate variability (HRV), a marker of cardiac autonomic function, and cognitive impairment.
Design: Cross-sectional analysis of baseline data from Women's Health and Aging Study I.
Setting: Urban community in Baltimore, Maryland.
Participants: A subset of 311 physically disabled, community-dwelling women aged 65 and older whose HRV data were obtained.
Measurements: Reduced HRV was defined as the lowest quartile of each of several HRV measures exploring time and frequency domains and compared with the remaining three quartiles. Cognitive impairment was defined as a Mini-Mental State Examination score less than 24. Multiple logistic regression was used to model the independent relationship between reduced HRV and prevalent cognitive impairment.
Results: The age-, education-, and race-adjusted prevalence of cognitive impairment was higher in those with reduced HRV than in those with nonreduced HRV. After adjusting for relevant demographic and clinical characteristics, participants with reduced HRV were significantly more likely than those with nonreduced HRV to have cognitive impairment; these findings were consistent across different HRV indices. In particular, reduced high-frequency power, indicative of decreased parasympathetic activity, was associated with 6.7 times greater odds of cognitive impairment (95% confidence interval = 2.27-20.0).
Conclusion: Cardiac autonomic dysfunction, particularly decreased parasympathetic activity, was independently associated with cognitive impairment in older disabled women in the community. This finding may improve understanding of the pathophysiological basis of cognitive impairment. The potential role of HRV as a cause or consequence of cognitive impairment needs to be elucidated in future studies.
Figures
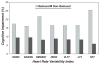
References
-
- National Institute on Aging, National Institutes of Health. Progress Report on Alzheimer’s Disease. NIH Publication no. 004859 [on-line] [Accessed May 4, 2005]. Available at www.alzheimers.org/pubs/prog00.htm#References.
-
- Graham JE, Rockwood K, Beattie BL, et al. Prevalence and severity of cognitive impairment with and without dementia in an elderly population. Lancet. 1997;349:1793–1796. - PubMed
-
- Launer LJ. The epidemiologic study of dementia: A life-long quest? Neurobiol Aging. 2005;26:335–340. - PubMed
-
- Heart rate variability: Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Circulation. 1996;93:1043–1065. - PubMed
-
- Nolan J, Batin PD, Andrews R, et al. Prospective study of heart rate variability and mortality in chronic heart failure: Results of the United Kingdom heart failure evaluation and assessment of risk trial (UK-heart) Circulation. 1998;98:1510–1516. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

