Refined spatial manipulation of neuronal function by combinatorial restriction of transgene expression
- PMID: 17088209
- PMCID: PMC1713190
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.08.028
Refined spatial manipulation of neuronal function by combinatorial restriction of transgene expression
Abstract
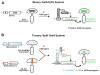
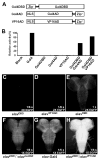
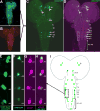
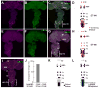
Selective genetic manipulation of neuronal function in vivo requires techniques for targeting gene expression to specific cells. Existing systems accomplish this using the promoters of endogenous genes to drive expression of transgenes directly in cells of interest or, in "binary" systems, to drive expression of a transcription factor or recombinase that subsequently activates the expression of other transgenes. All such techniques are constrained by the limited specificity of the available promoters. We introduce here a combinatorial system in which the DNA-binding (DBD) and transcription-activation (AD) domains of a transcription factor are independently targeted using two different promoters. The domains heterodimerize to become transcriptionally competent and thus drive transgene expression only at the intersection of the expression patterns of the two promoters. We use this system to dissect a neuronal network in Drosophila by selectively targeting expression of the cell death gene reaper to subsets of neurons within the network.
Figures




References
-
- Awatramani R, Soriano P, Rodriguez C, Mai JJ, Dymecki SM. Cryptic boundaries in roof plate and choroid plexus identified by intersectional gene activation. Nat Genet. 2003;35:70–75. - PubMed
-
- Bellen HJ, O'Kane CJ, Wilson C, Grossniklaus U, Pearson RK, Gehring WJ. P-element-mediated enhancer detection: a versatile method to study development in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1989;3:1288–1300. - PubMed
-
- Brand AH, Perrimon N. Targeted Gene-Expression As A Means Of Altering Cell Fates And Generating Dominant Phenotypes. Development. 1993;118:401–415. - PubMed
-
- Brent R, Ptashne M. A eukaryotic transcriptional activator bearing the DNA specificity of a prokaryotic repressor. Cell. 1985;43:729–736. - PubMed
-
- Cahill MA, Ernst WH, Janknecht R, Nordheim A. Regulatory Squelching. Febs Letters. 1994;344:105–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

