Identification of the alpha2-delta-1 subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels as a molecular target for pain mediating the analgesic actions of pregabalin
- PMID: 17088553
- PMCID: PMC1859964
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0409066103
Identification of the alpha2-delta-1 subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels as a molecular target for pain mediating the analgesic actions of pregabalin
Abstract
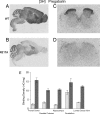
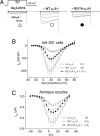
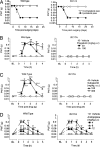
Neuropathic pain is a debilitating condition affecting millions of people around the world and is defined as pain that follows a lesion or dysfunction of the nervous system. This type of pain is difficult to treat, but the novel compounds pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin) have proven clinical efficacy. Unlike traditional analgesics such as nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs or narcotics, these agents have no frank antiinflammatory actions and no effect on physiological pain. Although extensive preclinical studies have led to a number of suggestions, until recently their mechanism of action has not been clearly defined. Here, we describe studies on the analgesic effects of pregabalin in a mutant mouse containing a single-point mutation within the gene encoding a specific auxiliary subunit protein (alpha2-delta-1) of voltage-dependent calcium channels. The mice demonstrate normal pain phenotypes and typical responses to other analgesic drugs. We show that the mutation leads to a significant reduction in the binding affinity of pregabalin in the brain and spinal cord and the loss of its analgesic efficacy. These studies show conclusively that the analgesic actions of pregabalin are mediated through the alpha2-delta-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels and establish this subunit as a therapeutic target for pain control.
Conflict of interest statement
A Conflict of interest statement: M.J.F., P.J.C., E.S., H.M., J.O., T.-Z.S., S.B., L.C., S.E., J.W., R.A.K., T.W., and D.W. are scientists in the employment of Pfizer Research and Development and own stock/have stock options for Pfizer Inc.
Figures

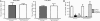
References
-
- Dworkin RH, Corbin AE, Young JP, Jr, Sharma U, LaMoreaux L, Bockbrader H, Garofalo EA, Poole RM. Neurology. 2003;60:1274–1283. - PubMed
-
- Farrar JT, Young JP, Jr, LaMoreaux L, Werth JL, Poole RM. Pain. 2001;94:149–158. - PubMed
-
- Selak I. Curr Opin Invest Drugs. 2001;2:828–834. - PubMed
-
- Lauria-Horner BA, Pohl RB. Exp Opin Invest Drugs. 2003;12:663–672. - PubMed
-
- Pande AC, Davidson JR, Jefferson JW, Janney CA, Katzelnick DJ, Weisler RH, Greist JH, Sutherland SM. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1999;19:341–348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

