Elevated tumour interleukin-1beta is associated with systemic inflammation: A marker of reduced survival in gastro-oesophageal cancer
- PMID: 17088911
- PMCID: PMC2360731
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603446
Elevated tumour interleukin-1beta is associated with systemic inflammation: A marker of reduced survival in gastro-oesophageal cancer
Abstract
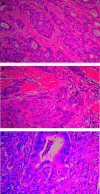
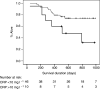
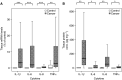
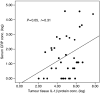
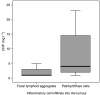
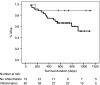
Systemic inflammation is associated with adverse prognosis cancer but its aetiology remains unclear. We investigated the expression of proinflammatory cytokines within normal mucosa from healthy controls and tumour tissue in cancer patients and related these levels with markers of systemic inflammation and with the presence of a tumour inflammatory infiltrate. Tissue was collected from 56 patients with gastro-oesophageal cancer and from 12 healthy controls. Tissue cytokine mRNA concentrations were measured by real-time PCR and tissue protein concentrations by cytometric bead array. The degree of chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate was recorded. Serum cytokine and acute phase protein concentrations (including C-reactive protein (CRP)) were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Proinflammatory cytokines were significantly overexpressed (interleukin (IL)-1beta, IL-6, IL-8 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha) both at mRNA and protein levels in the cancer specimens compared with mucosa from controls. Interleukin-1beta was expressed in greatest (10-100-fold) concentration and protein levels correlated significantly with systemic inflammation (CRP) (P = 0.05, r = 0.31). A chronic inflammatory infiltrate was observed in 75% of the cancer specimens and was associated with systemic inflammation (CRP: P = 0.01). However, the presence of chronic inflammation per se was not associated with altered cytokine expression within the tumour. Both a chronic inflammatory infiltrate and systemic inflammation (CRP) were associated with reduced survival (P = 0.05 and P = 0.03, respectively). Tumour chronic inflammatory infiltrate and tumour tissue IL-1beta overexpression are potential independent factors influencing systemic inflammation in oesophagogastric cancer patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radical gastric cancer surgery results in widespread upregulation of pro-tumourigenic intraperitoneal cytokines.ANZ J Surg. 2018 May;88(5):E370-E376. doi: 10.1111/ans.14267. Epub 2017 Nov 30. ANZ J Surg. 2018. PMID: 29194906
-
Host cytokine genotype is related to adverse prognosis and systemic inflammation in gastro-oesophageal cancer.Ann Surg Oncol. 2007 Feb;14(2):329-39. doi: 10.1245/s10434-006-9122-9. Epub 2006 Nov 11. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17103073
-
Prognostic implications of RASAL1 expression in oesophagogastric adenocarcinoma.J Clin Pathol. 2017 Mar;70(3):274-276. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2016-204132. Epub 2016 Dec 23. J Clin Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28011578 No abstract available.
-
Pathogenetic role and clinical significance of interleukin-1β in cancer.Immunology. 2023 Feb;168(2):203-216. doi: 10.1111/imm.13486. Epub 2022 May 7. Immunology. 2023. PMID: 35462425 Review.
-
Exploring Potential Biomarkers in Oesophageal Cancer: A Comprehensive Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 11;25(8):4253. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084253. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673838 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The expression and prognostic impact of CXC-chemokines in stage II and III colorectal cancer epithelial and stromal tissue.Br J Cancer. 2011 Feb 1;104(3):480-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6606055. Br J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21285972 Free PMC article.
-
Mutual amplification of HNF4α and IL-1R1 composes an inflammatory circuit in Helicobacter pylori associated gastric carcinogenesis.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 8;7(10):11349-63. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7239. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26870992 Free PMC article.
-
Tumorigenicity of IL-1alpha- and IL-1beta-deficient fibrosarcoma cells.Neoplasia. 2008 Jun;10(6):549-62. doi: 10.1593/neo.08286. Neoplasia. 2008. PMID: 18516292 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation and cancer: how friendly is the relationship for cancer patients?Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009 Aug;9(4):351-69. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2009.06.020. Epub 2009 Aug 6. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19665429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VCP phosphorylation-dependent interaction partners prevent apoptosis in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55724. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055724. Epub 2013 Jan 31. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23383273 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barber MD, Fearon KC, Ross JA (1999) Relationship of serum levels of interleukin-6, soluble interleukin-6 receptor and tumour necrosis factor receptors to the acute-phase protein response in advanced pancreatic cancer. Clin Sci (London) 96(1): 83–87 - PubMed
-
- Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254 - PubMed
-
- Bustin SA (2000) Absolute quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. J Mol Endocrinol 25: 169–193 - PubMed
-
- Chen JJ, Lin YC, Yao PL, Yuan A, Chen HY, Chien CT, Chen WJ, Lee YT, Yang PC (2005) Tumour-associated macrophages: the double-edged sword in cancer progression. J Clin Oncol 23(5): 953–964 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

