Group B Streptococcus: global incidence and vaccine development
- PMID: 17088932
- PMCID: PMC2742968
- DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro1552
Group B Streptococcus: global incidence and vaccine development
Abstract
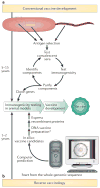
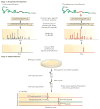
An ongoing public health challenge is to develop vaccines that are effective against infectious diseases that have global relevance. Vaccines against serotypes of group B Streptococcus (GBS) that are prevalent in the United States and Europe are not optimally efficacious against serotypes common to other parts of the world. New technologies and innovative approaches are being used to identify GBS antigens that overcome serotype-specificity and that could form the basis of a globally effective vaccine against this opportunistic pathogen. This Review highlights efforts towards this goal and describes a template that can be followed to develop vaccines against other bacterial pathogens.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Dermer P, Lee C, Eggert J, Few B. A history of neonatal group B streptococcus with its related morbidity and mortality rates in the United States. J Pediatr Nurs. 2004;19:357–363. - PubMed
-
- Edwards MS, Baker CJ. Group B Streptococcal infections in elderly adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41:839–847. - PubMed
-
An excellent review providing in-depth information on GBS infection in elderly adults.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

