Immunolocalization and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFRs) and neuropilins (NRPs) on keratinocytes in human epidermis
- PMID: 17088944
- PMCID: PMC1626599
- DOI: 10.2119/2006-00024.Man
Immunolocalization and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFRs) and neuropilins (NRPs) on keratinocytes in human epidermis
Abstract
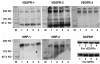
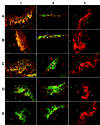
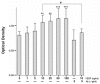
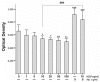
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) plays an important role in normal and pathological angiogenesis. VEGF receptors (VEGFRs, including VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, and VEGFR-3) and neuropilins (NRPs, including NRP-1 and NRP-2) are high-affinity receptors for VEGF and are typically considered to be specific for endothelial cells. Here we showed expression of VEGFRs and NRPs on cultured epidermal keratinocytes at both mRNA and protein levels. We further localized these receptors by immunofluorescence (IF) staining in the epidermis of surgical skin specimens. We found positive staining for VEGFRs and NRPs in all layers of the epidermis except for the stratum corneum. VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 are primarily expressed on the cytoplasmic membrane of basal cells and the adjacent spinosum keratinocytes. All layers of the epidermis except for the horny cell layer demonstrated a uniform pattern of VEGFR-3, NRP-1, and NRP-2. Sections staining for NRP-1 and NRP-2 also showed diffuse intense fluorescence and were localized to the cell membrane and cytoplasm of keratinocytes. In another panel of experiments, keratinocytes were treated with different concentrations of VEGF, with or without VEGFR-2 neutralizing antibody in culture. VEGF enhanced the proliferation and migration of keratinocytes, and these effects were partially inhibited by pretreatment with VEGFR-2 neutralizing antibody. Adhesion of keratinocytes to type IV collagen-coated culture plates was decreased by VEGF treatment, but this reduction could be completely reversed by pretreatment with VEGFR-2 neutralizing antibody. Taken together, our results suggest that the expression of VEGFRs and NRPs on keratinocytes may constitute important regulators for its activity and may possibly be responsible for the autocrine signaling in the epidermis.
Figures


References
-
- Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev. 2004;25:581–611. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P, Tessier-Lavigne M. Common mechanisms of nerve and blood vessel wiring. Nature. 2005;436:193–200. - PubMed
-
- Stacker SA, Achen MA. The vascular endothelial growth factor family: signalling for vascular development. Growth Factors. 1999;17:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Veikkola T, Alitalo K. VEGFs, receptors and angiogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol. 1999;9:211–20. - PubMed
-
- Neufeld G, Cohen T, Gengrinovitch S, Poltorak Z. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptors. FASEB J. 1999;13:9–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
