Response of neuroblastoma cells to ionizing radiation: modulation of in vitro invasiveness and angiogenesis of human microvascular endothelial cells
- PMID: 17088992
- PMCID: PMC2441915
Response of neuroblastoma cells to ionizing radiation: modulation of in vitro invasiveness and angiogenesis of human microvascular endothelial cells
Abstract
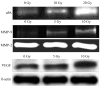
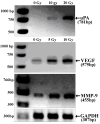
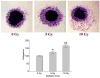
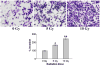
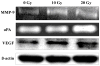
Neuroblastomas are the most common extra-cranial tumors of childhood and well known for their heterogeneous clinical behavior associated with certain genetic aberrations. Radiation therapy is an important modality for the treatment of high-risk neuroblastomas. In this study, we investigated whether ionizing irradiation modulate the migration and invasiveness of human neuroblastoma cells and expression of proangiogenic molecules known to be involved in tumor progression and metastasis. Irradiation of neuroblastoma cells resulted in increased migration and invasion as measured by spheroid migration and matrigel invasion assay respectively. Zymographic analysis revealed an increase in enzyme activity of MMP-9 and uPA in conditioned medium of irradiated neuroblastoma cells compared with non-irradiated cells. An increase in VEGF levels was also found in lysates of irradiated neuroblastoma cells. The up-regulation of uPA, MMP-9 and VEGF transcripts was also confirmed by RT-PCR analysis. Next, we examined the irradiated tumor cell-mediated modulation of endothelial cell behavior. Conditioned media from irradiated neuroblastoma cells enhanced capillary-like structure formation of microvascular endothelial cells. In a coculture system, irradiation of neuroblastoma cells enhanced endothelial cell invasiveness through Matrigel matrix. Endothelial cells treated with irradiated tumor cell conditioned medium were also analyzed for expression of uPA, MMP-9 and VEGF and compared to cells treated with non-irradiated tumor cell conditioned medium. These findings suggest that the irradiation effects of tumor cells could influence endothelial angiogenesis present in non-irradiated fields.
Figures


References
-
- Maris JM, Matthay KK. Molecular biology of neuroblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:2264–2279. - PubMed
-
- Escobar MA, Grosfeld JL, Powell RL, West KW, Scherer LR, 3rd, Fallon RJ, Rescorla FJ. Long-term outcomes in patients with stage IV neuroblastoma. J Pediatr Surg. 2006;41:377–381. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt ML, Lukens JN, Seeger RC, Brodeur GM, Shimada H, Gerbing RB, Stram DO, Perez C, Haase GM, Matthay KK. Biologic factors determine prognosis in infants with stage IV neuroblastoma: A prospective Children's Cancer Group study. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:1260–1268. - PubMed
-
- Laprie A, Michon J, Hartmann O, Munzer C, Leclair MD, Coze C, Valteau-Couanet D, Plantaz D, Carrie C, Habrand JL, Bergeron C, Chastagner P, Defachelles AS, Delattre O, Combaret V, Benard J, Perel Y, Gandemer V, Rubie H. Neuroblastoma Study Group of the French Society of Pediatric Oncology. High-dose chemotherapy followed by locoregional irradiation improves the outcome of patients with international neuroblastoma staging system Stage II and III neuroblastoma with MYCN amplification. Cancer. 2004;101:1081–1089. - PubMed
-
- Escobar MA, Grosfeld JL, Powell RL, West KW, Scherer LR, 3rd, Fallon RJ, Rescorla FJ. Long-term outcomes in patients with stage IV neuroblastoma. J Pediatr Surg. 2006;41:377–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

